Welcome to another hagiography of an acdemic career built on fabricated research results, brought to you by Smut Clyde. Today’s Photoshop hero is professor Yogeshwer Shukla, a highly distinguished Indian expert of toxicology, cancer research, proteomics and recently also nanotechnology, where he announced to cure cancer with nanoparticles soaked in Ayurvedically-relevant plant extracts. Shukla spent his entire career at the CSIR-Indian Institute of Toxicology Research (IITR) in Lucknow, where he has practised his art for almost 35 years since his early days of PhD in 1984, and where he now made it as Chief Scientist of Food, Drug and Chemical Toxicology.
The man who is not afraid to use a mango or even a pomegranate to kill cancer, received awards from the Indian Society of Health, Environment, Education and Research, for his Photoshop contributions in the field of cancer chemoprevention. Shukla, who probably will proclaim resveratrol’s antioxidative powers even after his 5th bottle of red wine, also used to be the General Secretary of Environmental Mutagen Society of India and the Indian Society of Toxicology. Despite having published oodles of peer-reviewed artworks, Professor Shukla’s due recognition in form of retractions was so far unjustly sparse: just 3, one for plagiarism in 2012 and two for data falsification in 2019.
![Screenshot_2019-05-29 Retraction notice to Theaflavins induced apoptosis of LNCaP cells is mediated through induction of p5[...]](https://forbetterscience.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/05/screenshot_2019-05-29-retraction-notice-to-theaflavins-induced-apoptosis-of-lncap-cells-is-mediated-through-induction-of-p5....png?w=950)
Professor Shukla’s visits abroad were rare and brief, like to WHO-IARC in Lyon, maybe his hosts didn’t like the competition. The great moustache wearer, now aged 55, rather prefers admirers to come to him. He organised the annual meeting of Environmental Mutagen Society of India in 2002 and in 2005, and more recently, was appointed as the Organising Secretary for the next year’s Environmental Mutagen Society of India in 2020. This eulogy is meant to promote Professor Shukla’s academic reputation and national fame to some new heights he might have never expected to reach.

Another green world, by Smut Clyde
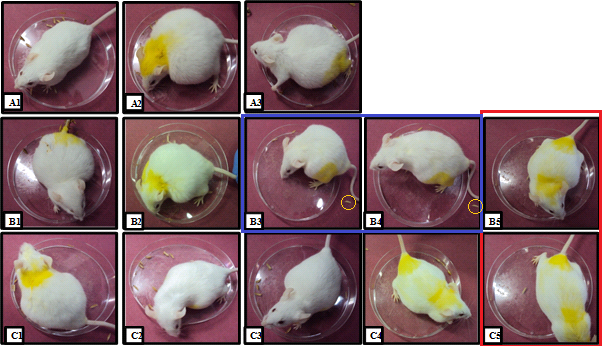
These mice were treated for cancer in 2014, using nano-encapsulated pineapple-squeezed bromelain (VII and VIII are identical twins) [1].
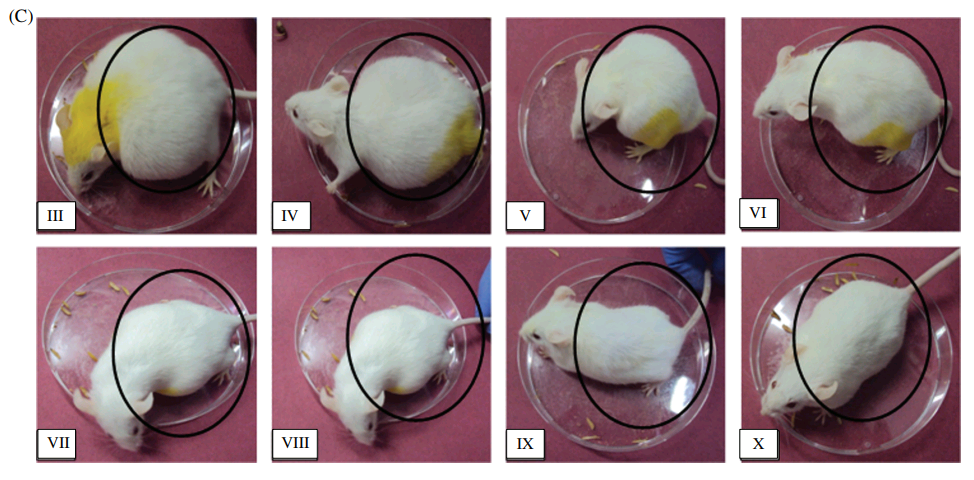
Not only was the treatment successful, but it prolonged their lives long past the usual murine span so they could be treated for cancer again in 2018, this time using nano-encapsulated barberry squeezings [2].
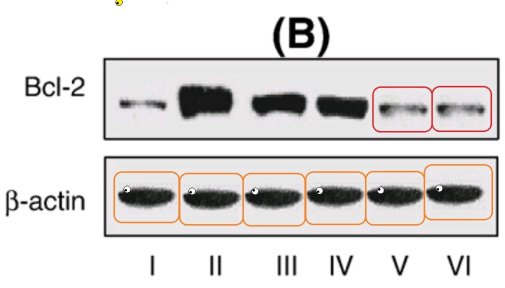
 Some uncertainly lingered whether the nano-encapsulation involved “Hyaluronic acid-grafted PLGA” or “O-Hexadecyl-Dextran” [3].
Some uncertainly lingered whether the nano-encapsulation involved “Hyaluronic acid-grafted PLGA” or “O-Hexadecyl-Dextran” [3].
The history of “medicinal pineapple” is in fact an interest of mine (I suspect it may be inspired by the verbal resonance between Ananas and Ananias, the patron saint of liars). It began with a German charlatan who reasoned that Bromelain is a meat-softening enzyme. and tumours are made of meat. Anyway, our rodent friends provide a convenient entry point to the cuisine-based corpus of Professor Yogeshwer Shukla at CSIR-Indian Institute of Toxicology Research (Delhi, India). For with the help of his colleagues and students, Dr Shukla has reported diverse botanical treatments for cancer (in mice!) in the course of his illustrious career… with squeezings from garlic, pomegranates, and mangos as well as pineapples. Also grape-skins and tea-leaves; and extracts from cinnamon, ginger and turmeric. Sometimes in isolation, sometimes in synergistic combination. It is as if an unlikely concatenation of events had led to the acceptance of a nouvelle-cuisine cookbook as a grant proposal.
As is the custom of my people, I shall draw heavily on comments left at the ‘PubPeer’ website, where 40 threads are currently devoted to discussing specific papers from his oeuvre. Some of those papers have been retracted, but surprisingly few in light of the unabashed data frauds they display. I can promise a promenade of hedgehogs, in illustration of Clyde’s First Law (“Everything is better with googly eyes”) [4].
But gratification deferred is gratification doubled, and to heighten the dramatic tension I’ll begin with a peripheral figure: Sahdeo Prasad, now Instructor at Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center, one shudders to think what he instructs people in, given his own record. The PubPeer archives for Prasad namely show him participating in much of the output from Shukla’s output — perhaps as a grad or post-grad student — around 2007-2009, a notably productive period for the laboratory. After that he ascended to the MD Anderson Cancer Center (University of Texas) to work with Bharat Aggarwal and co-author a string of papers, later retracted because the amount of fabrication in them exceeded editorial tolerance. Prasad now collaborates with the mendacious scoundrels at OMICS, and also edits journal-shaped dumpsters for Longdom Publishing (an OMICS polyp).
 Now Aggarwal’s name should be familiar. He was a pioneer in the field of ‘Jurisprudential Science’, which is where you prove the validity of your theories and results by issuing bumptious, censorious legal threats against your critics. If Jurisprudential Science is not yet the title of a parasitical journal from OMICS, it should be. Disgrace as a con-man and departure from the MD Anderson did not greatly discommode Aggarwal’s career. He continued to publish in Frontiers journals (aided by the complaisance of his quondam colleagues as editors and reviewers), and to star as a guest speaker at magical-thinking scamborees on “curing cancer with culturally-significant herbs and spices”.
Now Aggarwal’s name should be familiar. He was a pioneer in the field of ‘Jurisprudential Science’, which is where you prove the validity of your theories and results by issuing bumptious, censorious legal threats against your critics. If Jurisprudential Science is not yet the title of a parasitical journal from OMICS, it should be. Disgrace as a con-man and departure from the MD Anderson did not greatly discommode Aggarwal’s career. He continued to publish in Frontiers journals (aided by the complaisance of his quondam colleagues as editors and reviewers), and to star as a guest speaker at magical-thinking scamborees on “curing cancer with culturally-significant herbs and spices”.
Many of the Prasad / Aggarwal impostures emerged from a research goal of finding curative benefits from turmeric (more exactly, from the dyestuff / secondary metabolite curcumin extracted from turmeric), obliging them to fake results because in practice curcumin is a shite drug. Aggarwal also played a role in in the Red-Wine bubble… I do not mean the beaded bubbles winking at the brim of a beaker of blushful Hippocrene, but rather, the swell of enthusiasm for the grape-skin component resveratrol which was going to lengthen lifetimes and cure heart disease and cancer by drinking red wine until people collectively tired of faking positive results.

 The relevance of this little digression is that Yogeshwer Shukla espouses the same “culturally-significant plant product” ethnocentric-pharmacognosy approach to drug development, attempting to bring his artistic practice under the protective aegis of Ayurveda (like Aggarwal, he plays up the medieval-herbalism aspect of the Ayurvedic scammocopoeia and plays down the arsenic / mercury / lead toxic-metal alchemy). It must be tempting for scientists in India to claim that their work vindicates Ayurvedic Traditional Knowledge, so that as champions of Vedic cultural virtues they can call on the political forces of ethnocentric chauvinism to keep themselves dismissal-proof despite incompetence or corruption. As it happens, herbs like caraway and dill are important in my culture, especially their secondary metabolites infused in alcohol, but I do not pretend that Akvavit botanicals are responsible for my unnaturally-extended life-span.
The relevance of this little digression is that Yogeshwer Shukla espouses the same “culturally-significant plant product” ethnocentric-pharmacognosy approach to drug development, attempting to bring his artistic practice under the protective aegis of Ayurveda (like Aggarwal, he plays up the medieval-herbalism aspect of the Ayurvedic scammocopoeia and plays down the arsenic / mercury / lead toxic-metal alchemy). It must be tempting for scientists in India to claim that their work vindicates Ayurvedic Traditional Knowledge, so that as champions of Vedic cultural virtues they can call on the political forces of ethnocentric chauvinism to keep themselves dismissal-proof despite incompetence or corruption. As it happens, herbs like caraway and dill are important in my culture, especially their secondary metabolites infused in alcohol, but I do not pretend that Akvavit botanicals are responsible for my unnaturally-extended life-span.
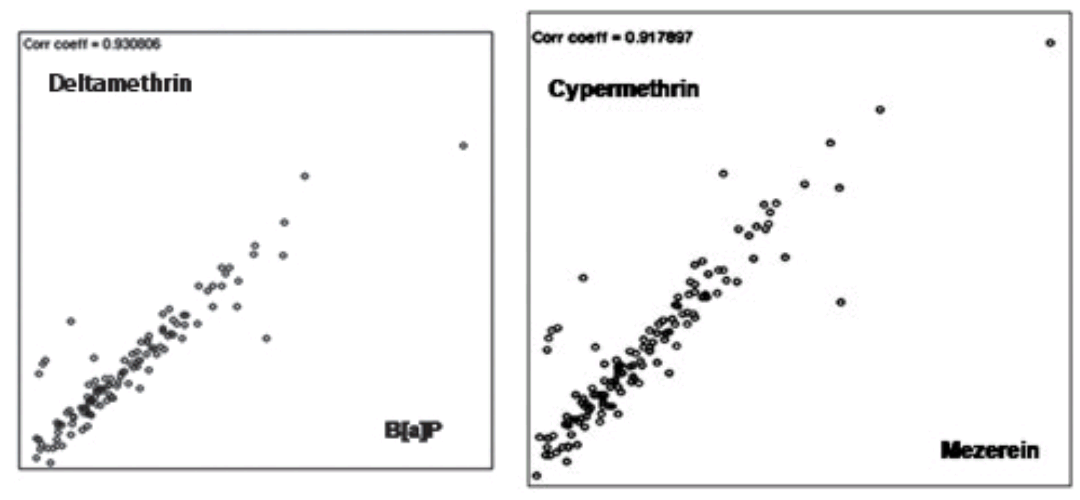
But back to the PubPeer archives. With so many threads, we can only scratch the surface of the iceberg on the seashore and divert ourselves in now and then finding a smoother pebble or a prettier shell than ordinary. Rest assured that curing cancer does not distract Dr Shukla entirely from the ‘Toxicology’ aspect of his institution, and he also studies the carcinogen side of the coin, even if he sometimes confuses Deltamethrin and Benz-α-pyrene, on one hand [5], with Cypermethrin and mezerein on the other [6].
So let’s start with a recent paper (2016) [7], in which the magic of mango squeezings (Lupeol) prevent a fungicide (Mancozeb) from causing cancer. Here are two panels from Figure 2. Now I am not wise in the ways of counting cells by fluorescence and graphing the results as a histogram, but I do know that histograms are supposed to be solid. If they are undercut by erosion or the ravages of termites (marked in red), something is wrong. It is also a problem if fine details are identical in what are purportedly independent experiments (marked in blue).
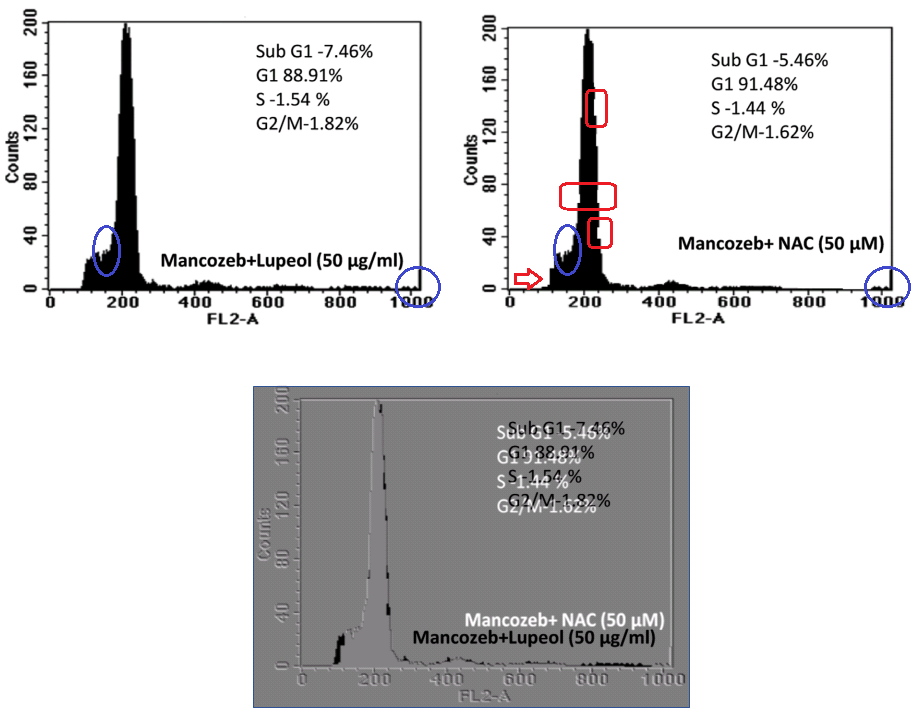
The pixels which were whittled away from the left-hand panel with the Eraser tool show up as black, after black / white reversing the right-hand panel and superimposing it on the former (everything else cancels out). This is MS Paint work, not even Photoshop! This clumsy, lazy falsification is a slap in the face for honest hard-working data forgers who take pride in their workmanship.
Here are earlier examples of white-anted overhanging histograms, from Fig 4A of [8] at left, while the outlined examples at right (from Figure 2 of [9]) are riddled with glitches, like free software:
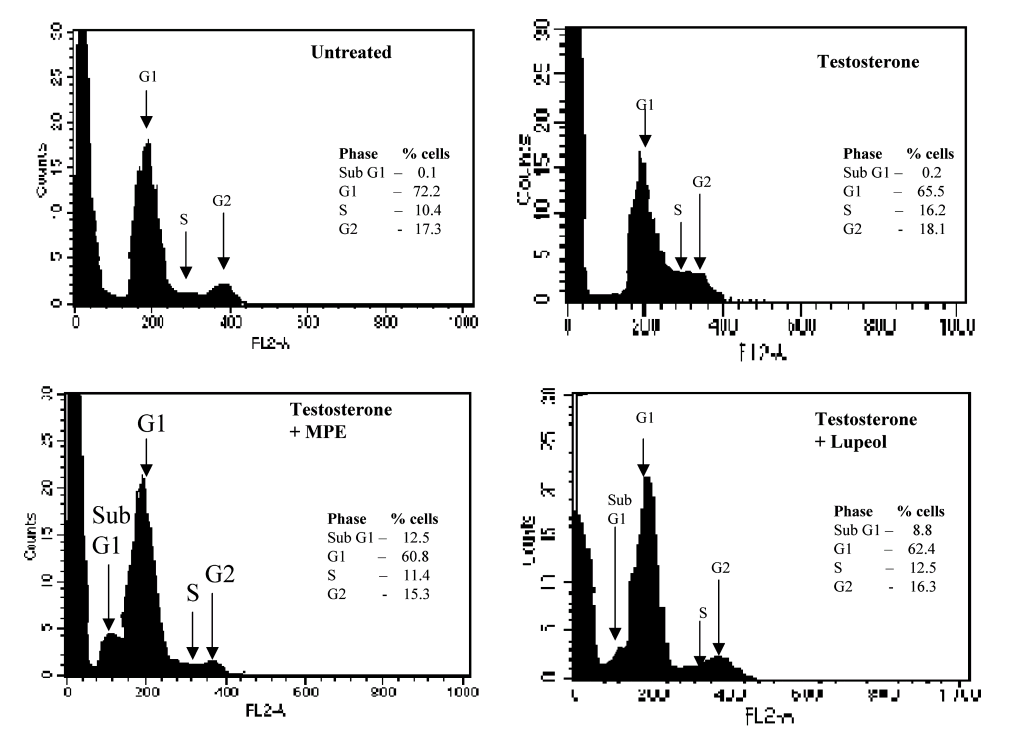
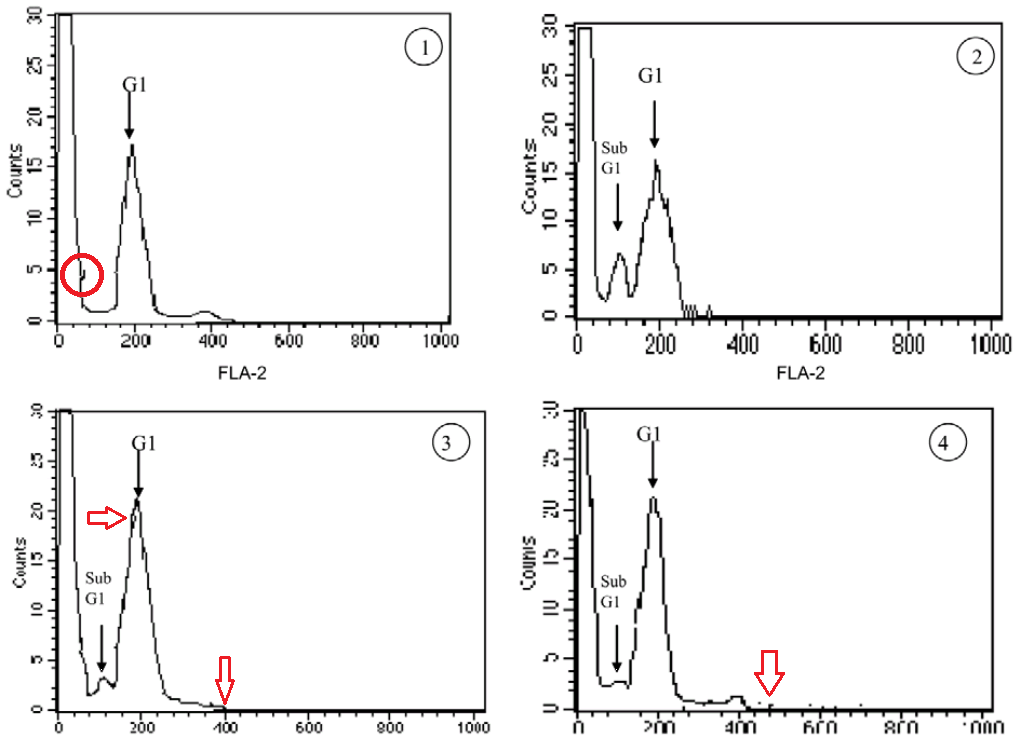
In fact these are snapshots in the process of carving cell-count histograms from scratch. They are like scenes from the creation of a sculpture or a painting, like watching Giaocometti scraping away the clay or pigment he had added in an earlier stage in the cycle. Now [8] still centred on mango juice, while [9] focused on the cancer-preventing powers of garlic… but an overlay of these supposedly-separate data sets shows the sections of perimeter which were not re-worked, and leaves one to wonder if there were any original data measurements at all.
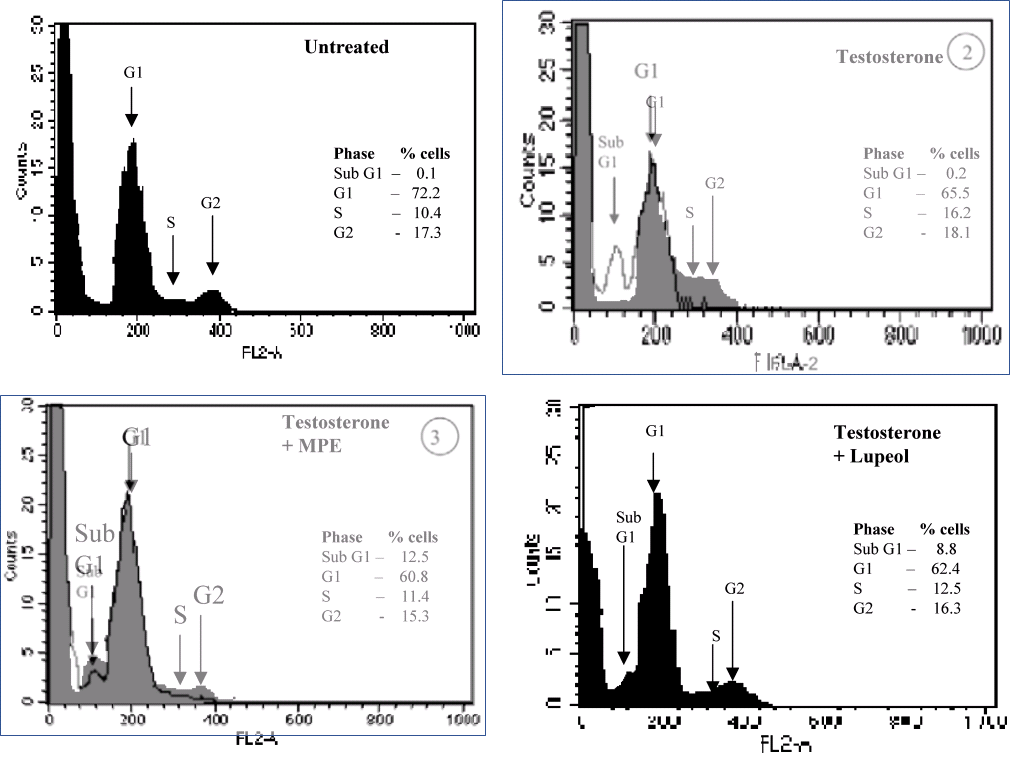
One last example before we move on. In contrast to the toppling minarets in Fig. 4A of [8], what renders 4B risible are similarities among its panels, where only a few pixels were scraped from one and added to another.

When we turn from to Figure 2 of [10], which at least still hoes the row of mango-juice cancer prevention (even though its protective powers are extended over mouse liver cells, rather than lymph node carcinoma of the prostate), it is not too great a surprise to encounter find cell-count plots that are outlined but superimposable.
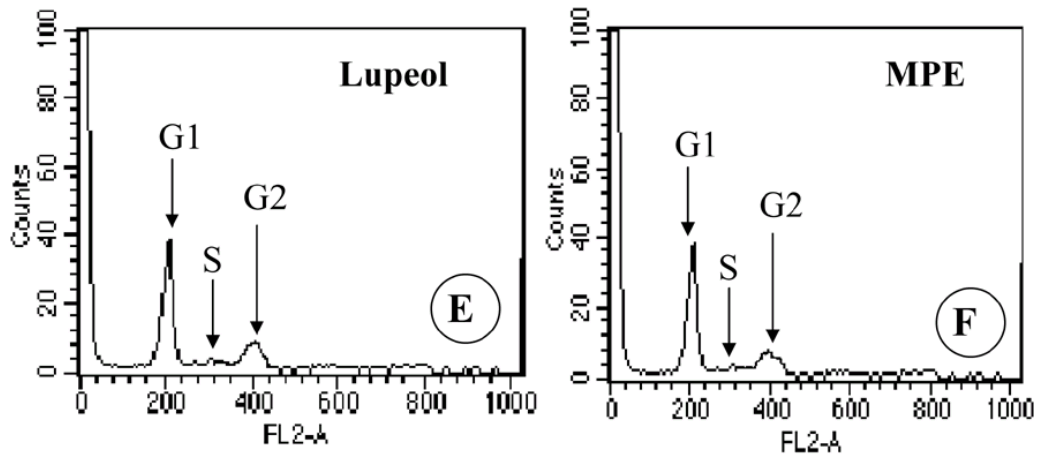
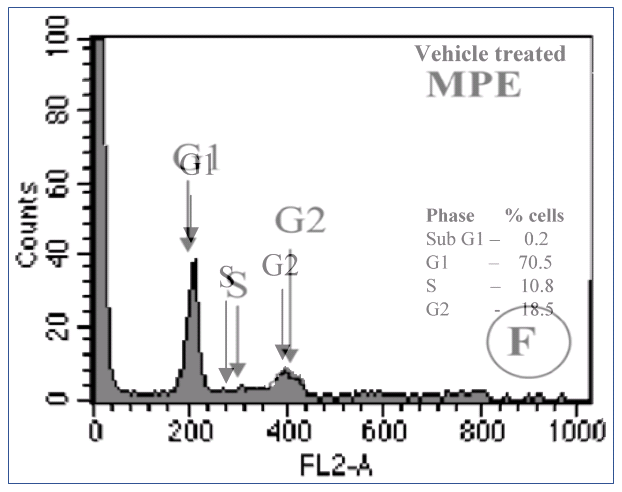
In contrast to histogrammed cell counts, flow-cytometry plots (FACS) measure two fluorescent indicators of each cell’s status and use them as coordinates to plot each cell as a point in two dimensions. They feature prominently in this body of work. They display a recurring quality of insufficient difference. Partial replications could arise when someone took a single file of data (recorded for one experimental condition) and ran it twice through different settings of the filter parameters… but also when someone modified a plot in Paint / Photoshop.
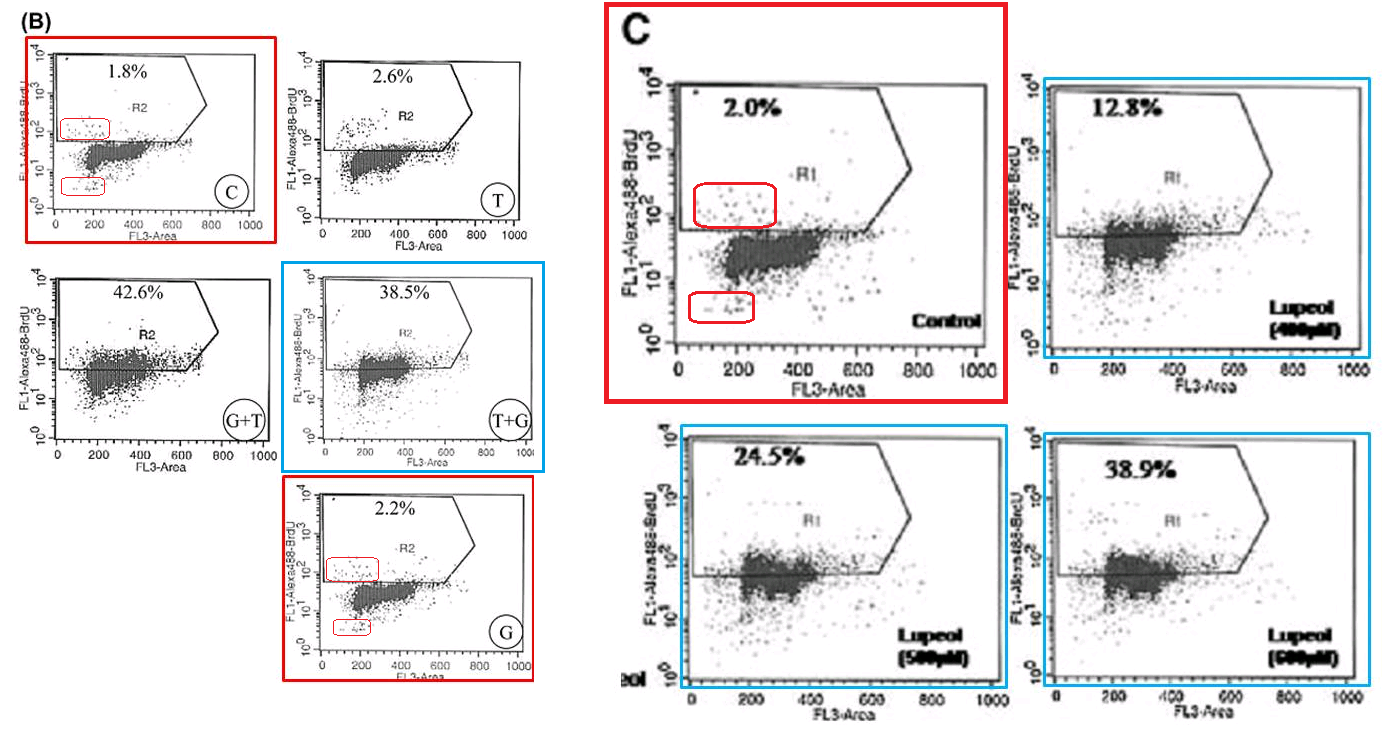
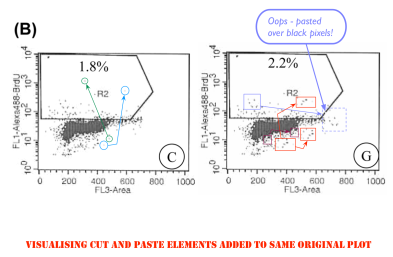
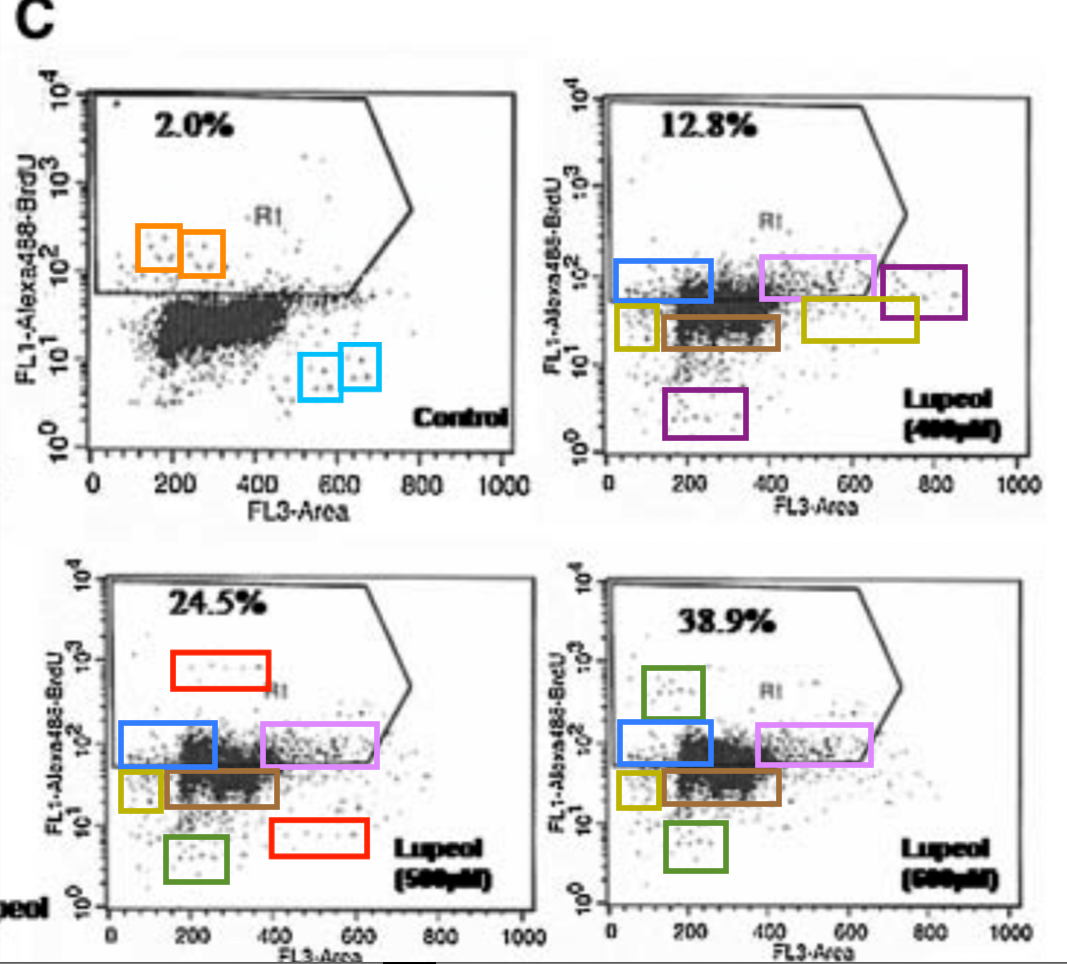
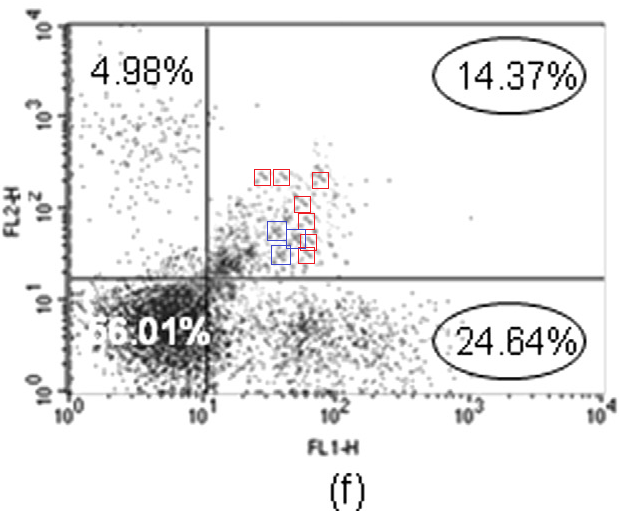
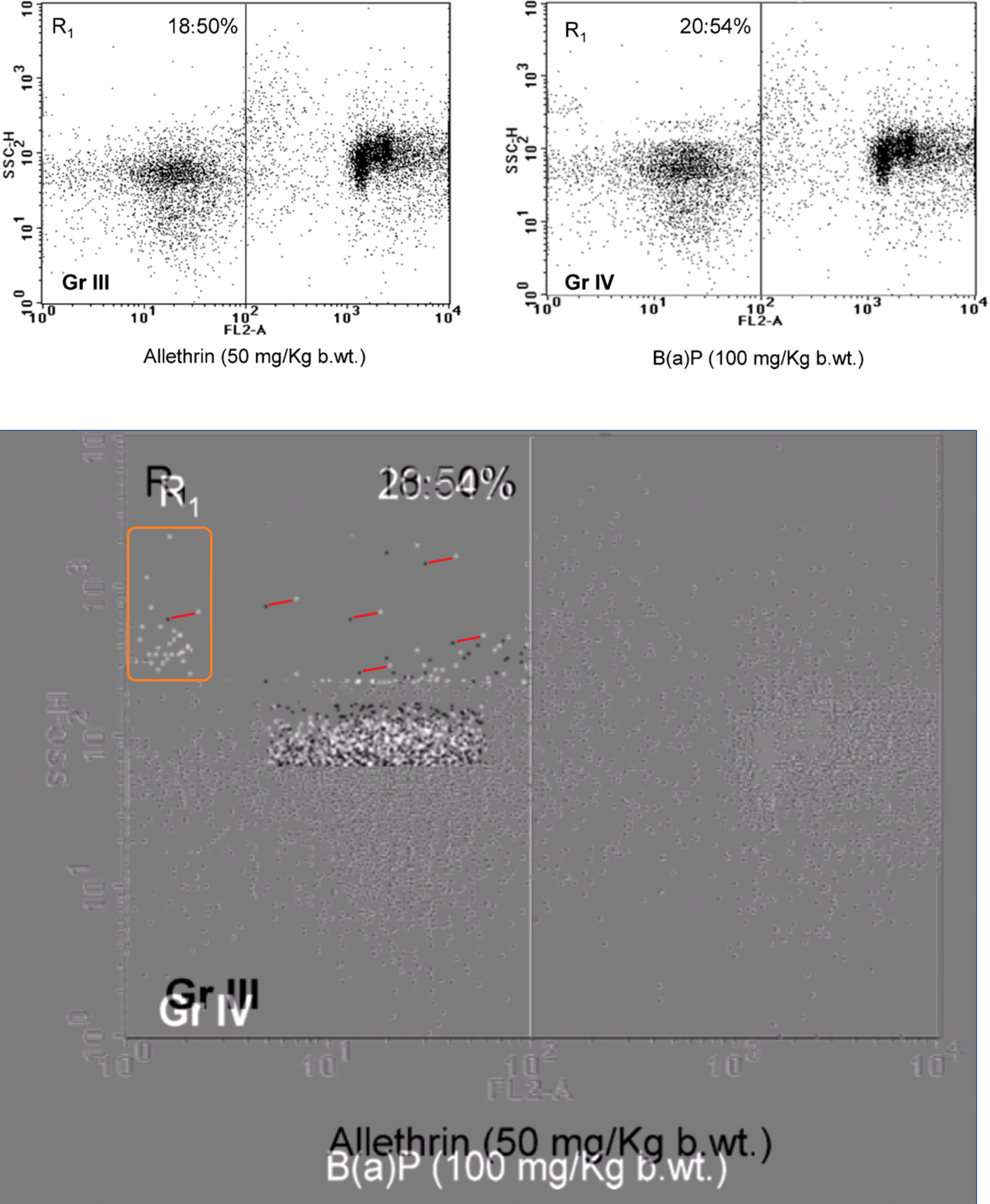 A good example is Figure 2 from a 2012 paper on the mutagenic mayhem wrought by Allethrin insecticide in the absence of mango protection. “Boeckella Robusta” wondered “could authors explain how the same dot plots were generated for different treatments in the indicated boxes?”
A good example is Figure 2 from a 2012 paper on the mutagenic mayhem wrought by Allethrin insecticide in the absence of mango protection. “Boeckella Robusta” wondered “could authors explain how the same dot plots were generated for different treatments in the indicated boxes?”
Indeed, in a superimposition of the Allethrin and Benz-α-pyrene panels, cancellation is complete across three quarters of the plane. There is a patch of white points unique to B-α-P treatment; an exact rectangle of discordant cells; and a zone of black/white pairs where cells were displaced en masse. The forger saw no need for anything sophisticated.
As for the Control panel, res ipsa loquitur.
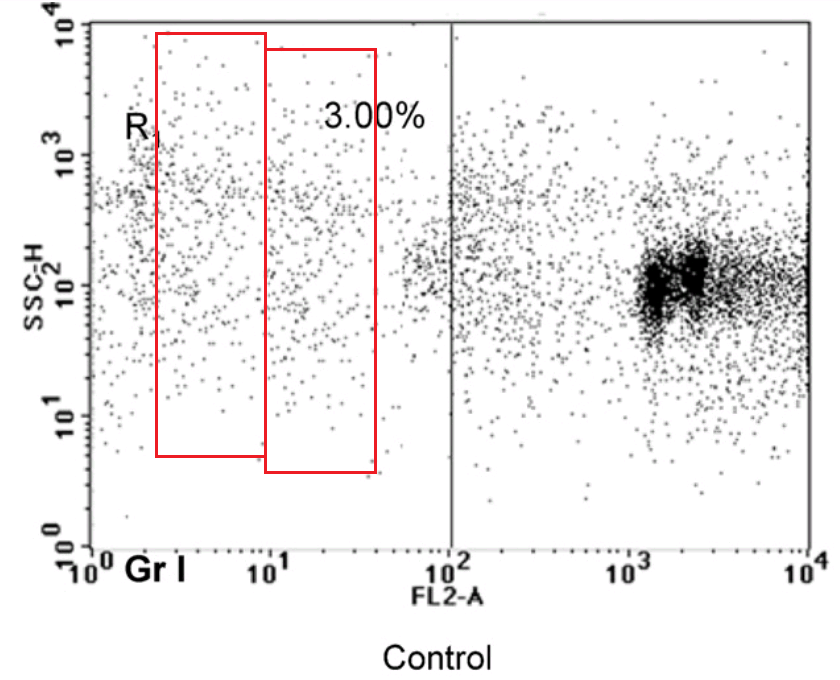
Paper [1] from 2014 gave us the curative nano-pineapples. As “Notarius Cookei” noted, it also provides examples of FACS fakery. Here I choose Figures 6(G) and 6(H), and 9(F) and 9(H).

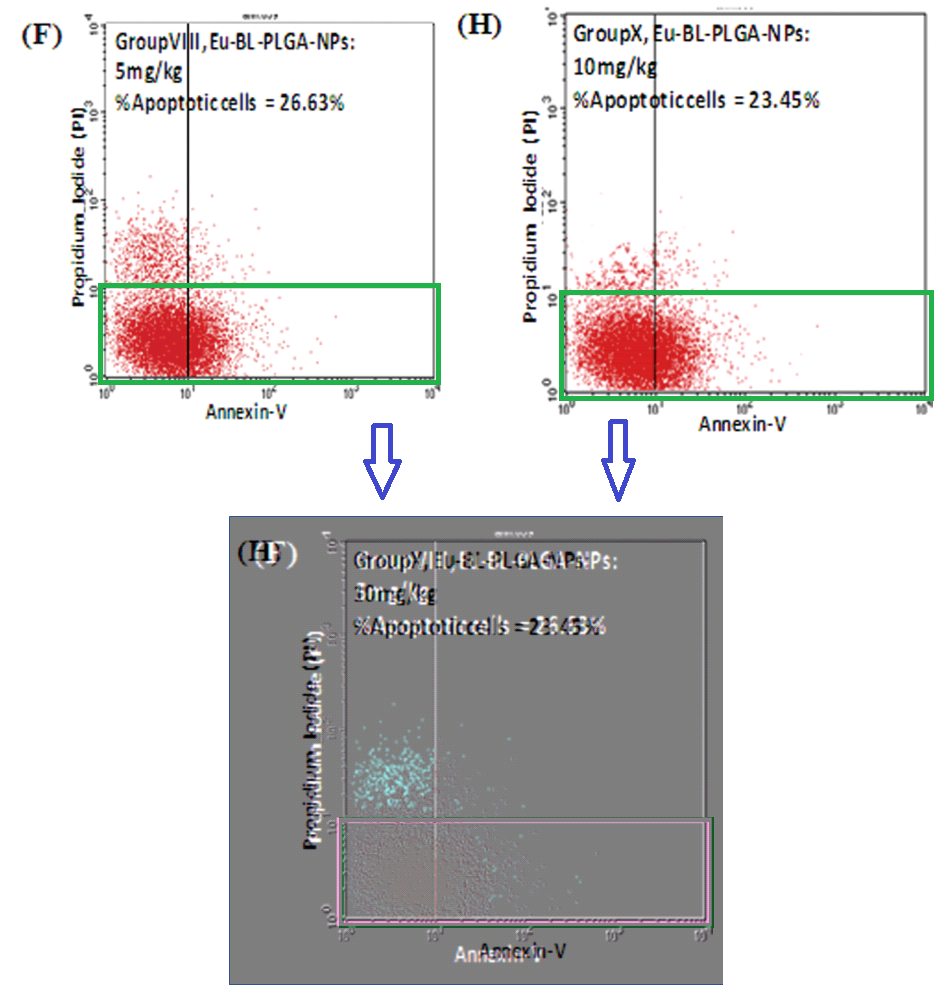
“When 99% of cells are identical in both plots, the most parsimonious explanation is that both plots used the same data.”
I skip over other examples in my haste to reach the delirious heights of [12] and [13]. These companion papers from 2007 and 2008 fed ginger and mangos respectively through the juicer, but the authors liked the FACS plots so much that they used them in both.
Then someone customised and enhanced each version, cloning clusters of points with all the enthusiasm of a child who has just been introduced to the artistic possibilities of the potato-stamp medium. Figures 5(B) of [12] and 4(C) of [13] should be enlarged to appreciate their plenitude.
Another spurt of potato-stamp creativity occurred in 2011, in the panels of Figure 6 of [14]. The prospect of inhibiting the growth of skin tumours (in mice) with a synergistic combination of grape-skins and black tea evidently distracted the reviewers’ attentions from the crystalline alignment of the FACS plots.

It also emerged that garlic and pomegranates, together, exerted exactly the same inhibition, resulting in a companion paper [15]. I do not rate for this recipe.

A lot of work went into these constructions, possibly more than simply conducting an experiment would require, so one can understand the authors’ decision to repeat them across papers. Suffice to say that the cloning tool contributed to Figure 6 of [15].


Regrettably, [14] was retracted in April for a number of reasons (not just Figure 6). The world of science was thereby deprived of a row of hot-dogs comprising the ERK1/2 band of Figure 2.
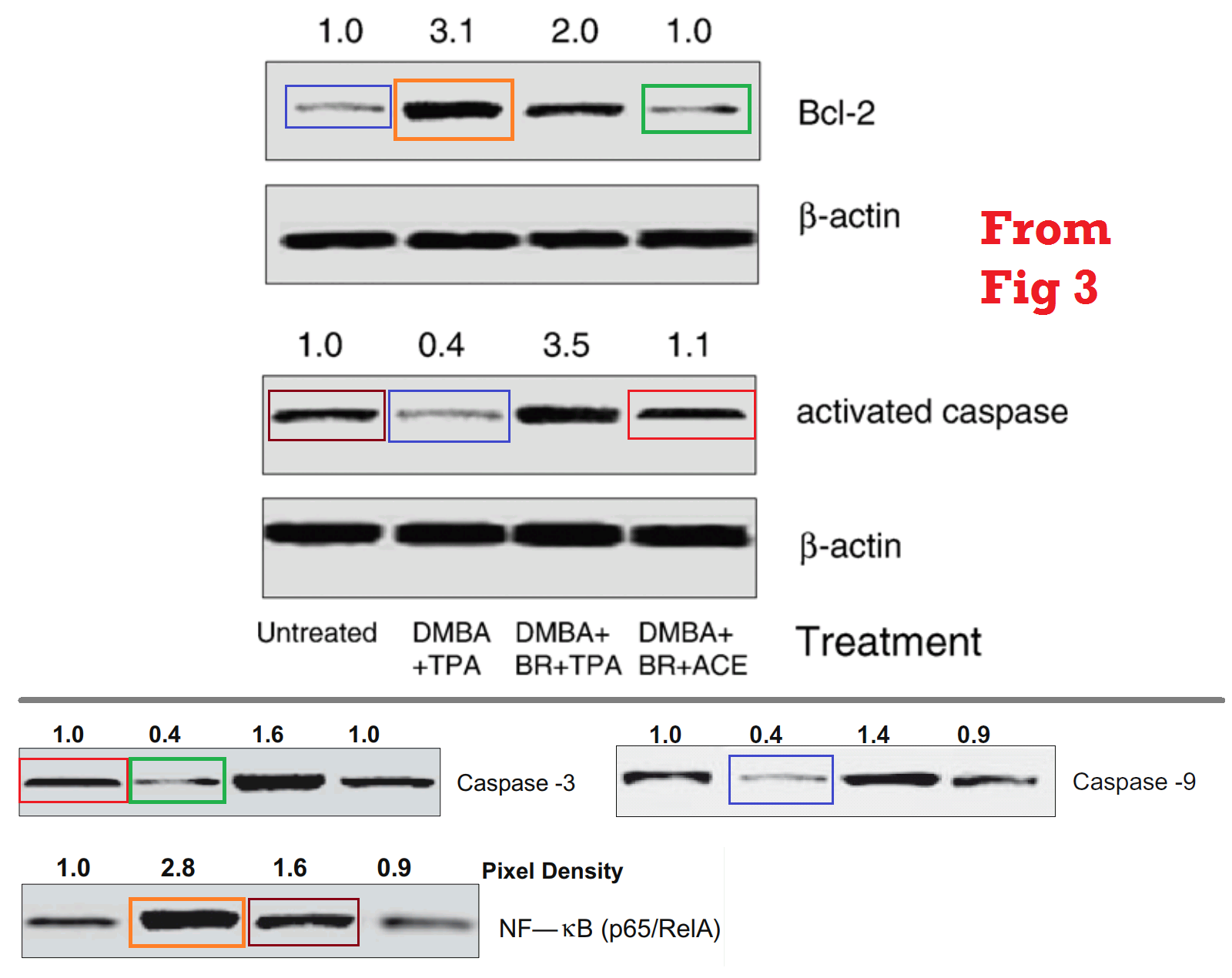
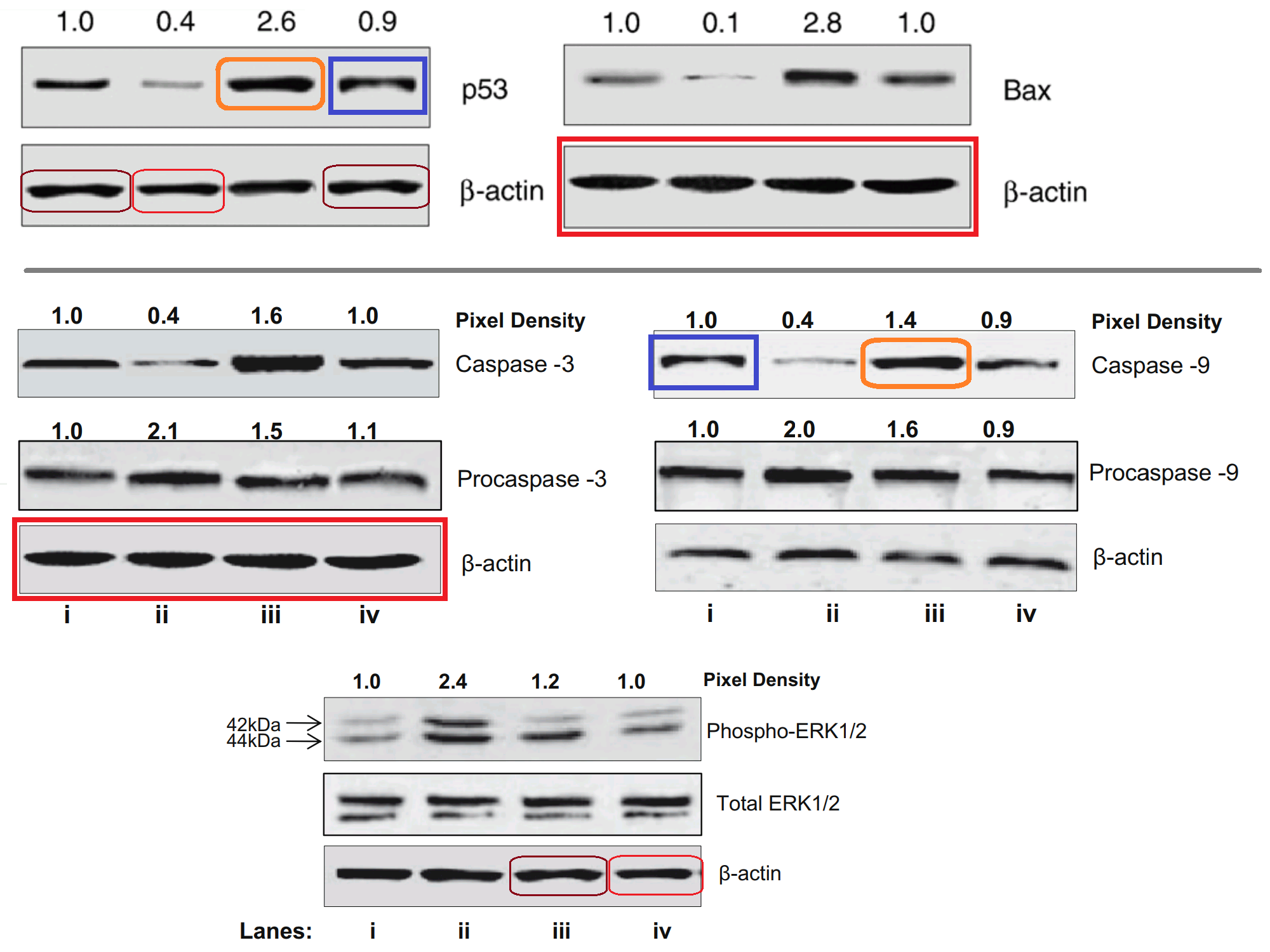
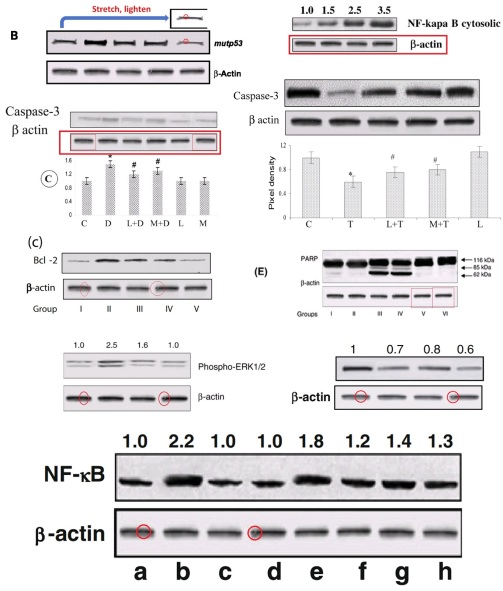
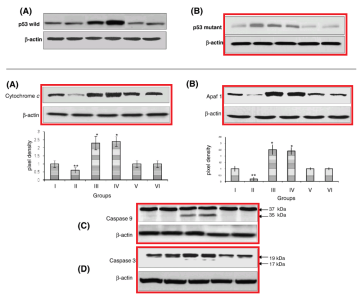
These provide a segue to the inevitable Western-blot discussion. For this body of work has its fair share of gel bands with acrobatic talents, somersaulting and stretching and reflecting as they re-identify from one Protean protein to another (and from one paper to another). Figures 3, 4 and 6 from [16]:
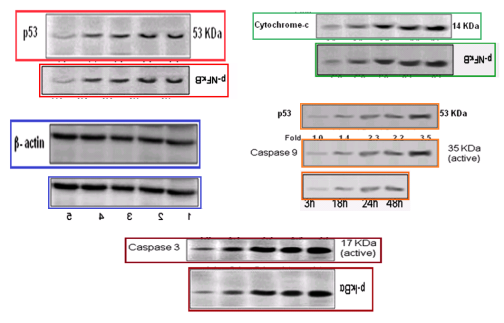
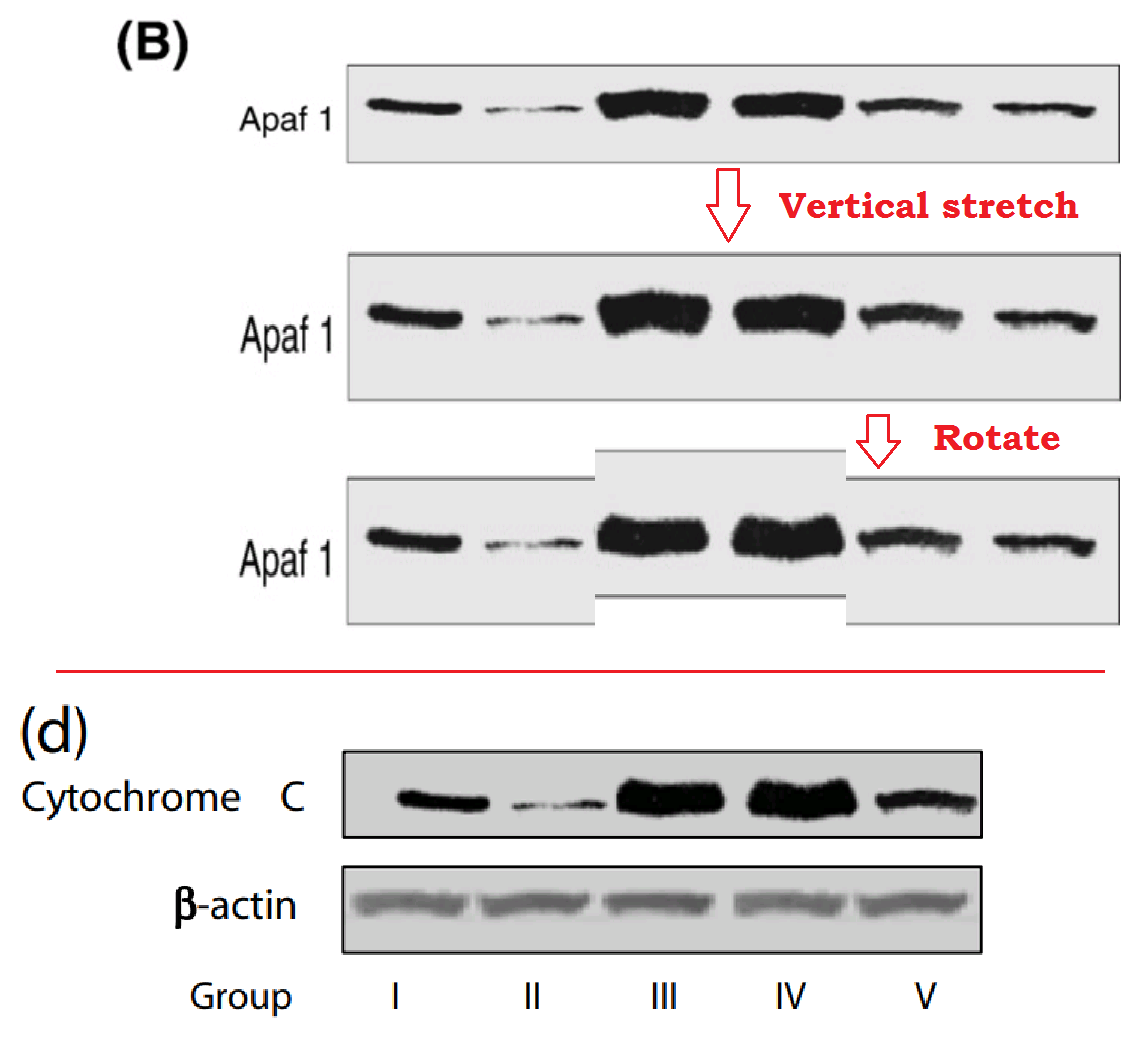
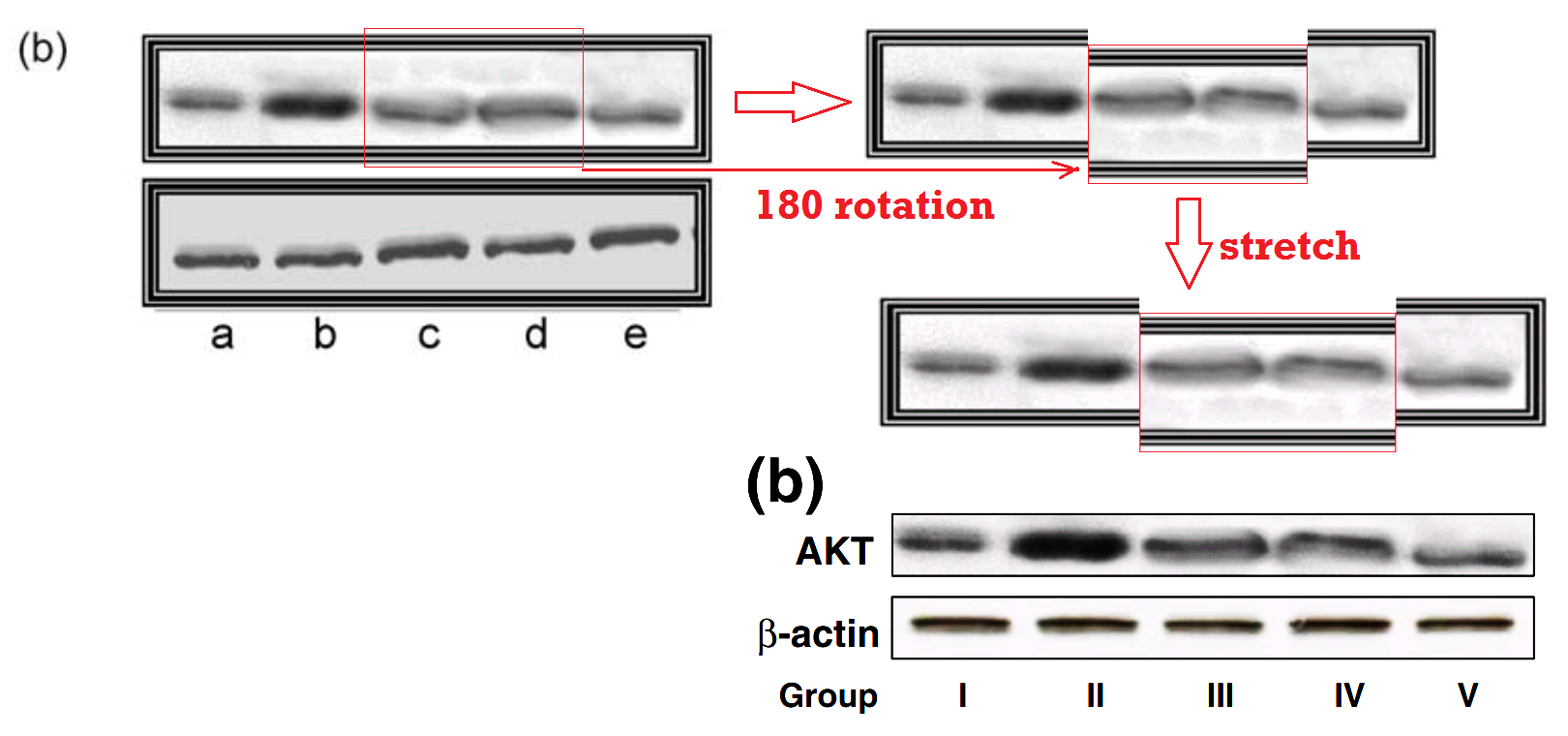
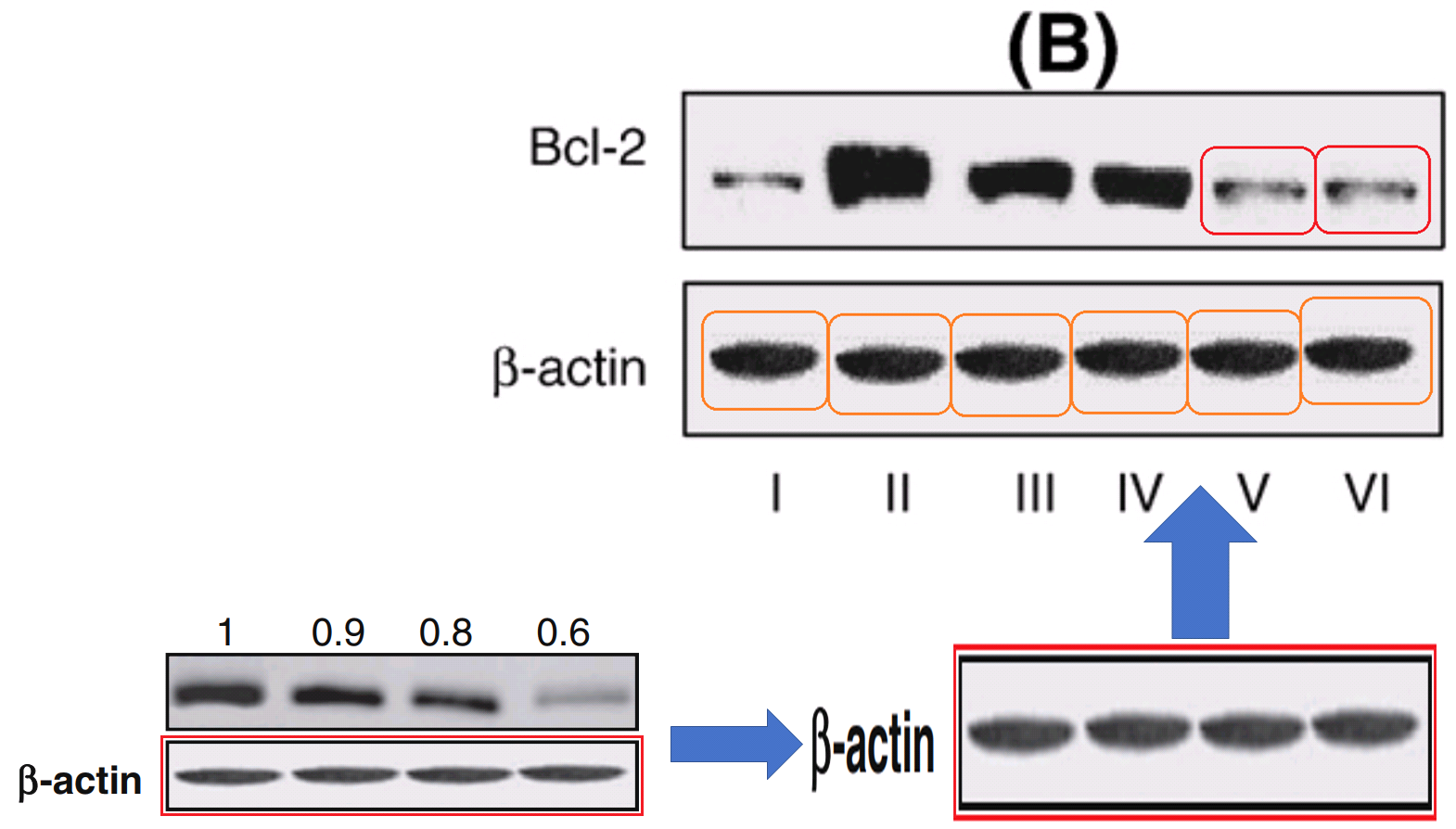
The next somersaults are lane-specific and require more skill. At left, Apaf 1 (from Fig 5B of [4]) becomes Cytochrome C (in Fig 3(d) of [17]). At right, p21/ras (from 2(b) of [18]) becomes AKT (in Fig 5(b) of [17])!
At one end of the spectrum of manipulation, blots might be repeated in successive figures with different labels, relying on the incuriosity of readers and reviewers. At the other extreme, they are cut up and reassembled like letters in a ransom note. Here from [19] to [20].
All this is for substantive protein measurements. The normalising controls fare no better. As interest in Shukla’s productions grew, ‘Orophea Enterocarpa‘ identified a small but hard-working repertoire of loading controls. The ‘bubble and hairline’ control, for instance, first spotted in 2004 with five lanes for five experimental levels of garlic [21], has at least nine recorded sightings, sometimes cut down to four lanes or extended to six with a lane duplication to meet the details of the study design. These lanes corresponded to dosage of tea [22, 24], mango / lupeol [8, 10], grape-skins [4, 17, 23] and pineapple [19]. In its most recent appearance (2010) it widened to an eight-lane Interstate highway.
The “scrolls” were another hard-worked loading-control panel with five sightings [8, 12, 17, 18, 22]. Sadly, there is not space to show the “inchworm” panel, or the “dotted dashes“, or the “Nike Swoosh“, or even the “dashes-and-dots” in their four- and eight-lane incarnations.
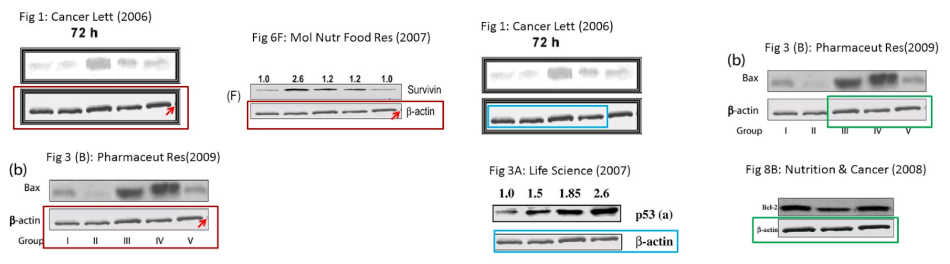
My favourite in this little genre began in 2008 as Fig 3(A) of [4], holding sway over six variants of grape-skin therapy. It reappeared as a four-lane version as Fig 1(B) of [20], a pineapple study (other panels of 1(B) also repay attention); and in Fig 3 of [19]. Pay attention to the third (or first) lane: for greater standardisation, it was quadruplicated in another 2009 loading control [23].
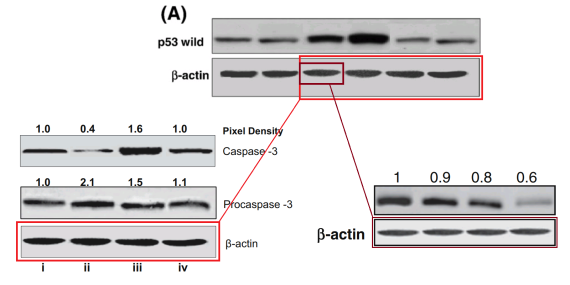
While back where we started, [4] also starred Fig 6(B), the “hedgehog promenade”. This proves to be another version of that single lane lane from 3(A), now multiplied six-fold and stretched vertically.
 Admittedly, not everyone agrees on the necessity for dose-equalising controls. Between publication of [4] in 2008 and an amendment in 2016, it had featured Figs 3(B) and 5, in which five-lane letterbox panels of β-actin sufficed to normalise a series of six-lane blots of interest. Either the readers and reviewers and editors couldn’t count or they didn’t care.
Admittedly, not everyone agrees on the necessity for dose-equalising controls. Between publication of [4] in 2008 and an amendment in 2016, it had featured Figs 3(B) and 5, in which five-lane letterbox panels of β-actin sufficed to normalise a series of six-lane blots of interest. Either the readers and reviewers and editors couldn’t count or they didn’t care.
Recall the point of compass-coded blotting methods: to quantify the protein expression within cells under specific conditions, by a circuitous but precise route (extracting cell contents and separating the proteins by racing them along an electrophoresis-gel racetrack or Proteodrome, then labelling them with antibodies so as to measure total antibody density). Now it is always possible that researchers did measure all the numbers they tabulate and analyse, producing blots in the process with which they could have illustrated their reports, and they only decide to fabricate the illustrations (or repurpose old ones) because of the artistic challenge.
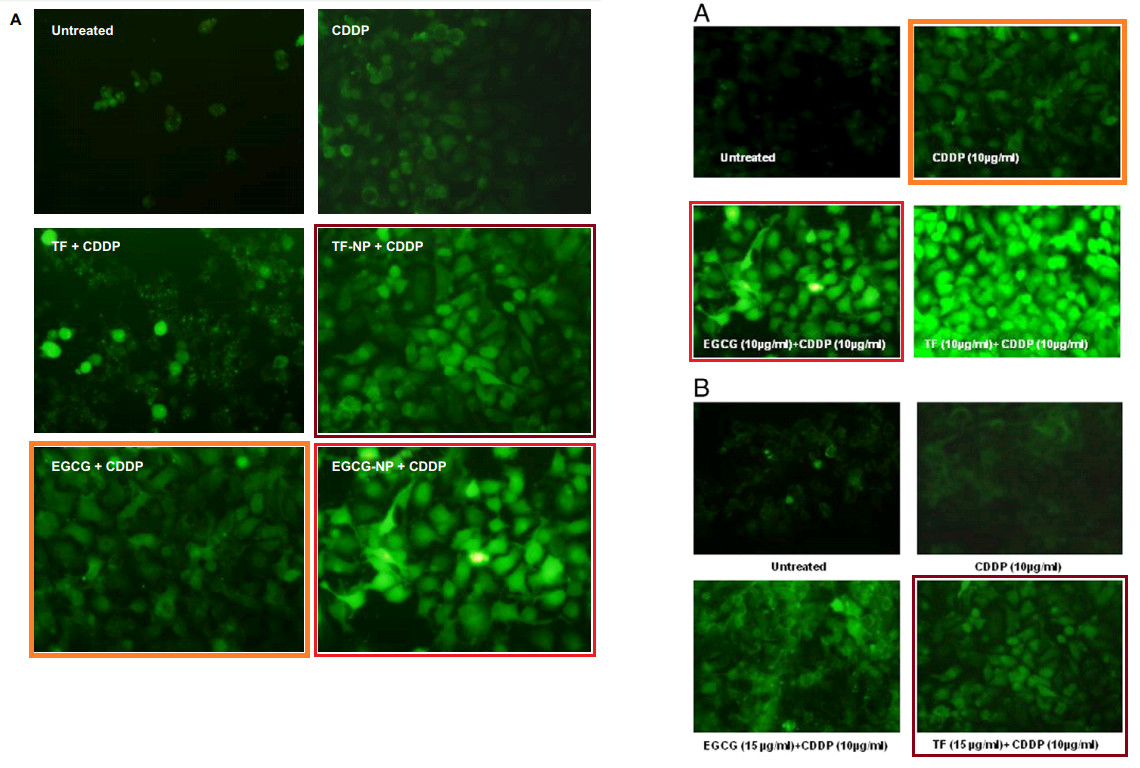
After all this, there is a sense of relief to be had from meeting plain microphotographs of vat-grown tumour cells from the A549 cell-line, rendered fluorescent by different treatment with black tea polyphenols [16]. Or perhaps they hailed from the HeLa and SiHa cell-lines [25].
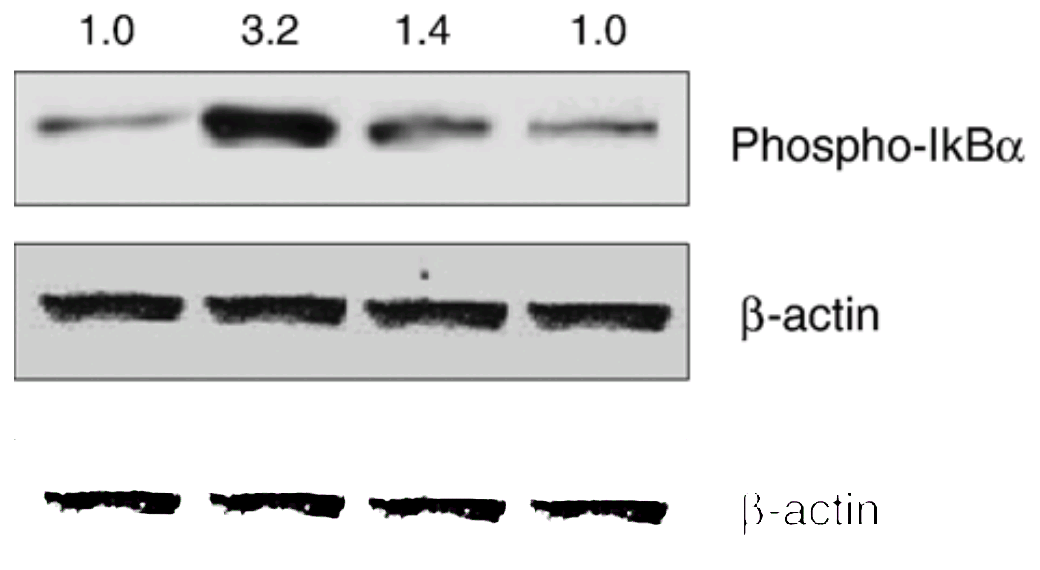 I had originally hoped to show some Northern blots of RNA expression (Caspase-3 becomes iκBα); or perhaps some DNA fragmentation assays, which display a lapidary, mosaic nature when closely examined. But this report is long enough. I must be content with this loading control from [19], which reminds me (when the lightness is turned up) of a row of caddis-fly larvae.
I had originally hoped to show some Northern blots of RNA expression (Caspase-3 becomes iκBα); or perhaps some DNA fragmentation assays, which display a lapidary, mosaic nature when closely examined. But this report is long enough. I must be content with this loading control from [19], which reminds me (when the lightness is turned up) of a row of caddis-fly larvae.
Now I am not alleging retouching or Photoshop manipulations, but there are two images of Dr Yogeshwer Shukla on the Intertubes. The version shown on his staff page at the CSIR-Indian Institute of Toxicology Research website has changed a lot from the version on his ResearchGate account.
If this is the effect of pineapple or mango or grape-skin treatment, he is his own best advertisement for his discoveries.
[1] Priyanka Bhatnagar, Soma Patnaik, Amit K. Srivastava, Mohan K. R. Mudiam, Yogeshwer Shukla, Amulya K. Panda, Aditya B. Pant, Pradeep Kumar, Kailash C. Gupta
Anti-Cancer Activity of Bromelain Nanoparticles by Oral Administration
Journal of Biomedical Nanotechnology (2014) doi: 10.1166/jbn.2014.1997
https://pubpeer.com/publications/D7569FE3179E5C77F10CD7D0CAFF1C
[2] Priyanka Bhatnagar, Manisha Kumari, Richa Pahuja, A. B. Pant, Y. Shukla, Pradeep Kumar, K. C. Gupta
Hyaluronic acid-grafted PLGA nanoparticles for the sustained delivery of berberine chloride for an efficient suppression of Ehrlich ascites tumors
Drug Delivery and Translational Research (2018) doi: 10.1007/s13346-018-0485-9
https://pubpeer.com/publications/17D26A485788CD2B46B52781D8DD50
[3] Radhika Kapoor, Shruti Singh, Madhulika Tripathi, Priyanka Bhatnagar, Poonam Kakkar, Kailash Chand Gupta
O-hexadecyl-dextran entrapped berberine nanoparticles abrogate high glucose stress induced apoptosis in primary rat hepatocytes
PLoS ONE (2014) doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0089124
https://pubpeer.com/publications/012D4D634C827AE2183864F22FD1A0
[4] Neetu Kalra, Preeti Roy, Sahdeo Prasad, Yogeshwer Shukla
Resveratrol induces apoptosis involving mitochondrial pathways in mouse skin tumorigenesis
Life Sciences (2008) doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2007.11.006
https://pubpeer.com/publications/4197501DBC472982247DE0AFA234E3
[5] Jasmine George, Yogeshwer Shukla
Early changes in proteome levels upon acute deltamethrin exposure in mammalian skin system associated with its neoplastic transformation potential
Journal of Toxicological Sciences (2013)
https://pubpeer.com/publications/F65D2C5FFC638303800927B2E28661
[6] Jasmine George, Amit Kumar Srivastava, Richa Singh, Yogeshwer Shukla
Cypermethrin exposure leads to regulation of proteins expression involved in neoplastic transformation in mouse skin
Proteomics (2011) doi: 10.1002/pmic.201100233
https://pubpeer.com/publications/A384A6D53974AF627FC83477C2D43E
[7] Amit Kumar Srivastava, Sanjay Mishra, Wahid Ali, Yogeshwer Shukla
Protective effects of lupeol against mancozeb-induced genotoxicity in cultured human lymphocytes
Phytomedicine (2016) doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2016.03.010
https://pubpeer.com/publications/5AA6712082CCC91EEE90C4C5196BFE
[8] Sahdeo Prasad, Neetu Kalra, Yogeshwer Shukla
Induction of apoptosis by lupeol and mango extract in mouse prostate and LNCaP cells
Nutrition & Cancer (2007) doi: 10.1080/01635580701613772
https://pubpeer.com/publications/5316531EB262091B243859A00C0137
[9] S Prasad, N Kalra, S Srivastava, Y Shukla
Regulation of oxidative stress–mediated apoptosis by diallyl sulfide in DMBA-exposed Swiss mice
Human & Experimental Toxicology (2008) doi: 10.1177/0960327108088978
https://pubpeer.com/publications/92E0808D22F88CCD9F6CB46ACC36A8
[10] Sahdeo Prasad, Neetu Kalra, Yogeshwer Shukla
Hepatoprotective effects of lupeol and mango pulp extract of carcinogen induced alteration in Swiss albino mice
Molecular Nutrition & Food Research (2007) doi: 10.1002/mnfr.200600113
https://pubpeer.com/publications/76E17585B48AC0B38E498B5EC23054
[11] Amit Kumar Srivastava, Pramod Kumar Srivastava, Abdulaziz A. Al-Khedhairy, Javed Musarrat, Yogeshwer Shukla
Allethrin-induced genotoxicity and oxidative stress in Swiss albino mice
Mutation Res/Fund Mol Mech Mutagenesis (2012) doi: 10.1016/j.mrgentox.2012.03.003
https://pubpeer.com/publications/3D8F9A166D74AE68A779582773B7AD
[12] Yogeshwer Shukla, Sahdeo Prasad, Chitra Tripathi, Madhulika Singh, Jasmine George, Neetu Kalra
In vitro and in vivo modulation of testosterone mediated alterations in apoptosis related proteins by [6]-gingerol
Molecular Nutrition & Food Research (2007) doi: 10.1002/mnfr.200700197
https://pubpeer.com/publications/F9BEECCBE9F74B9796BFA11F079FF9
[13] Sahdeo Prasad, Nidhi Nigam, Neetu Kalra, Yogeshwer Shukla
Regulation of signaling pathways involved in lupeol induced inhibition of proliferation and induction of apoptosis in human prostate cancer cells
Molecular Carcinogenesis (2008) doi: 10.1002/mc.20442
https://pubpeer.com/publications/977BFB109F38955F21E8259D74F9C0
[14] RETRACTED: Jasmine George, Madhulika Singh, Amit Kumar Srivastava, Kulpreet Bhui, Preeti Roy, Pranav Kumar Chaturvedi, Yogeshwer Shukla
Resveratrol and black tea polyphenol combination synergistically suppress mouse skin tumors growth by inhibition of activated MAPKs and p53
PLoS ONE (2011) doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0023395
https://pubpeer.com/publications/1ADC5417FEF462F17636A43498D670
[15] Jasmine George, Madhulika Singh, Amit Kumar Srivastava, Kulpreet Bhui, Yogeshwer Shukla
Synergistic growth inhibition of mouse skin tumors by pomegranate fruit extract and diallyl sulfide: evidence for inhibition of activated MAPKs/NF-κB and reduced cell proliferation
Food & Chemical Toxicology (2011) doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2011.03.040
https://pubpeer.com/publications/4A46821594EB7EB392F5A9BB471E5A
[16] Madhulika Singh, Kulpreet Bhui, Richa Singh, Yogeshwer Shukla
Tea polyphenols enhance cisplatin chemosensitivity in cervical cancer cells via induction of apoptosis
Life Sciences (2013) doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2013.02.001
https://pubpeer.com/publications/8BC7D198B330260105915A17A97BE7
[17] Preeti Roy, Neetu Kalra, Sahdeo Prasad, Jasmine George, Yogeshwer Shukla
Chemopreventive potential of resveratrol in mouse skin tumors through regulation of mitochondrial and PI3K/AKT signaling pathways
Pharmaceutical Research (2009) doi: 10.1007/s11095-008-9723-z
https://pubpeer.com/publications/850796C5228A56DF71E8D4E4601C87
[18] Annu Arora, Neetu Kalra, Yogeshwer Shukla
Regulation of p21/ras protein expression by diallyl sulfide in DMBA induced neoplastic changes in mouse skin
Cancer Letters (2006) doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2005.10.049
https://pubpeer.com/publications/A5216BB8F4E05BB3A05E274F56618B
[19] Neetu Kalra, Kulpreet Bhui, Preeti Roy, Smita Srivastava, Jasmine George, Sahdeo Prasad, Yogeshwer Shukla
Regulation of p53, nuclear factor kappaB and cyclooxygenase-2 expression by bromelain through targeting mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway in mouse skin
Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology (2008) doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2007.08.012
https://pubpeer.com/publications/4A3803831AE2603C9276ADB9750A85
[20] Kulpreet Bhui, Sahdeo Prasad, Jasmine George, Yogeshwer Shukla
Bromelain inhibits COX-2 expression by blocking the activation of MAPK regulated NF-kappa B against skin tumor-initiation triggering mitochondrial death pathway
Cancer Letters (2009) doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2009.03.003
https://pubpeer.com/publications/19913878F1C75788FE95D3FD1FCADE
[21] Annu Arora, Imtiaz A Siddiqui, Yogeshwer Shukla
Modulation of p53 in 7,12-dimethylbenz[a]anthracene-induced skin tumors by diallyl sulfide in Swiss albino mice
Molecular Cancer Therapeutics (2004)
https://pubpeer.com/publications/2DE54FD49EB1CAE22A11E768845A2C
[22] RETRACTED: Neetu Kalra, Kavita Seth, Sahdeo Prasad, Madhulika Singh, Aditya B. Pant, Yogeshwer Shukla
Theaflavins induced apoptosis of LNCaP cells is mediated through induction of p53, down-regulation of NF-kappa B and mitogen-activated protein kinases pathways
Life Sciences (2007) doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2007.04.009
https://pubpeer.com/publications/916B9A4E38D79FAF24E97FFB891AC8
[23] Preeti Roy, Esha Madan, Neetu Kalra, Nidhi Nigam, Jasmine George, Ratan Singh Ray, Rajendra K Hans, Sahdeo Prasad, Yogeshwer Shukla
Resveratrol enhances ultraviolet B-induced cell death through nuclear factor-kappaB pathway in human epidermoid carcinoma A431 cells
Biochem & Biophys Research Comm (2009) doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.04.100
https://pubpeer.com/publications/D9903CAA6326AC41B3A998B45FDFD7
[24] Preeti Roy, Nidhi Nigam, Madhulika Singh, Jasmine George, Smita Srivastava, Hasnain Naqvi, Yogeshwer Shukla
Tea polyphenols inhibit cyclooxygenase-2 expression and block activation of nuclear factor-kappa B and Akt in diethylnitrosoamine induced lung tumors in Swiss mice
Investigational New Drugs (2010) doi: 10.1007/s10637-009-9274-0
https://pubpeer.com/publications/202F3FCC1C55B94992B036E1761395
[25] Madhulika Singh, Priyanka Bhatnagar, Sanjay Mishra, Pradeep Kumar, Yogeshwer Shukla, Kailash Chand Gupta
PLGA-encapsulated tea polyphenols enhance the chemotherapeutic efficacy of cisplatin against human cancer cells and mice bearing Ehrlich ascites carcinoma
International Journal of Nanomedicine (2015) doi: 10.2147/ijn.s79489
https://pubpeer.com/publications/90ECC2BE7345B133B7E876E34801FB


Donate!
If you are interested to support my work, you can leave here a small tip of $5. Or several of small tips, just increase the amount as you like (2x=€10; 5x=€25). Your generous patronage of my journalism will be most appreciated!
€5.00




Large swathes of the western middle-class lap this stuff up. I think that the word “ayurvedic” really helps the scammers. Difficult to pronounce and difficult to spell. Once you say this word you are under its spell, which is what ayurvedic medicine is about.
LikeLike
Recent correction for “Inhibitory effects of tea polyphenols by targeting cyclooxygenase-2 through regulation of nuclear factor kappa B, Akt and p53 in rat mammary tumors” (Preeti Roy , Jasmine George , Smita Srivastava , Shilpa Tyagi , Yogeshwer Shukla; Investigational New Drugs, 2011).
https://pubpeer.com/publications/309118EE39149EF7FDAB4E323994A1
“The authors regret to inform that there were unknowing errors in figures. The corrected images are given below. These figures are not affecting the results and conclusion of the manuscript. Hence, the text in original paper remains unchanged.”
“Unknowing errors”.
LikeLike
https://thewire.in/the-sciences/csir-says-its-probing-scientific-misconduct-allegations-drafting-new-guidelines
“one common name on 49 of the articles was Yogeshwer Shukla, IITR’s chief scientist of food, drug and chemical toxicology. Shukla is a senior scientist, and has claimed to have cured cancer in mice using nano-encapsulated elements from plants with Ayurvedic relevance. Several of these claims, however, are now under question due to image manipulation.”
LikeLike
2020 retraction of
Mutat Res. 2012 Aug 30;747(1):22-28. doi: 10.1016/j.mrgentox.2012.03.003. Epub 2012 Mar 20.
Allethrin-induced genotoxicity and oxidative stress in Swiss albino mice.
Srivastava AK1, Srivastava PK2, Al-Khedhairy AA3, Musarrat J3, Shukla Y4.
Author information
1
Proteomics Laboratory, Indian Institute of Toxicology Research (CSIR), P.O. Box 80, M.G. Marg, Lucknow 226001, UP, India; Department of Biochemistry, Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi 221005, UP, India.
2
Department of Biochemistry, Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi 221005, UP, India.
3
Department of Zoology, College of Science, King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
4
Proteomics Laboratory, Indian Institute of Toxicology Research (CSIR), P.O. Box 80, M.G. Marg, Lucknow 226001, UP, India.
2020 retraction notice.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1383571819303742
This article has been retracted at the request of the Editor-in-Chief. In this article Figure 2 is described as depicting flow cytometry data of micronuclei induced by allethrin at different doses, but the figure contains duplications which affect the conclusions of the article. The authors have not been able to provide any justification for this image manipulation. As such this article represents a misuse of the scientific publishing system. The scientific community takes a very strong view on this matter and apologies are offered to readers of the journal that this was not detected during the submission process.
LikeLike
2020 retraction same institute.
https://www.jbc.org/content/295/9/2889
This article has been withdrawn by the authors. Portions of the LC3 immunoblot in Fig 2B overlap with Fig 3A. The Control and BPA (40μg/kg) images in Fig 2F are duplicates. Considering these issues, the authors state that the responsible course of action is to withdraw the article to uphold the high standards of publication ethics of the scientific literature from the author’s group and the Journal. The authors stand by the overall conclusions of the study and plan to republish the article with suitable changes in another journal.
J Biol Chem. 2015 Aug 21;290(34):21163-84. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.648998. Epub 2015 Jul 2.
Activation of Autophagic Flux against Xenoestrogen Bisphenol-A-induced Hippocampal Neurodegeneration via AMP kinase (AMPK)/Mammalian Target of Rapamycin (mTOR) Pathways.
Agarwal S1, Tiwari SK1, Seth B1, Yadav A1, Singh A2, Mudawal A1, Chauhan LK3, Gupta SK4, Choubey V5, Tripathi A6, Kumar A1, Ray RS4, Shukla S7, Parmar D1, Chaturvedi RK8.
Author information
1
From the Developmental Toxicology Laboratory, Systems Toxicology and Health Risk Assessment Group, CSIR-Indian Institute of Toxicology Research (CSIR-IITR), 80 MG Marg, Lucknow 226001, India, the Academy of Scientific and Innovative Research, CSIR-IITR Lucknow Campus, Lucknow 226001, India.
2
From the Developmental Toxicology Laboratory, Systems Toxicology and Health Risk Assessment Group, CSIR-Indian Institute of Toxicology Research (CSIR-IITR), 80 MG Marg, Lucknow 226001, India.
3
the Central Instrumentation Facility, CSIR-IITR, Lucknow 226001, India.
4
the Academy of Scientific and Innovative Research, CSIR-IITR Lucknow Campus, Lucknow 226001, India, the Systems Toxicology and Health Risk Assessment Group, CSIR-IITR, Lucknow 226001, India, and.
5
the Department of Pharmacology, Centre of Excellence for Translational Medicine, University of Tartu, Tartu, 50050 Estonia.
6
the Academy of Scientific and Innovative Research, CSIR-IITR Lucknow Campus, Lucknow 226001, India, the Food Drug and Chemical Toxicology Group, CSIR-IITR, Lucknow 226001, India.
7
the Department of Pharmacology, CSIR-Central Drug Research Institute, Sector 10, Jankipuram Extension, Lucknow 226031, India.
8
From the Developmental Toxicology Laboratory, Systems Toxicology and Health Risk Assessment Group, CSIR-Indian Institute of Toxicology Research (CSIR-IITR), 80 MG Marg, Lucknow 226001, India, the Academy of Scientific and Innovative Research, CSIR-IITR Lucknow Campus, Lucknow 226001, India, rajnish@iitr.res.in
LikeLike
“Professor Shukla’s due recognition in form of retractions was so far unjustly sparse: just 3, one for plagiarism in 2012 and two for data falsification in 2019.”
http://retractiondatabase.org/RetractionSearch.aspx?AspxAutoDetectCookieSupport=1#?AspxAutoDetectCookieSupport%3d1%26auth%3dShukla%252c%2bYogeshwer
To date 6 research articles retracted and 1 review article retracted.
Due recognition is gradually dawning.
LikeLike
2020 retraction for:
Mol Carcinog. 2008 Dec;47(12):916-24. doi: 10.1002/mc.20442.
Regulation of signaling pathways involved in lupeol induced inhibition of proliferation and induction of apoptosis in human prostate cancer cells.
Prasad S1, Nigam N, Kalra N, Shukla Y.
Author information
1
Proteomics Laboratory, Indian Institute of Toxicology Research, Lucknow, India.
2020 retraction notice.
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/mc.20442
The above article, published online on April 10 2008 in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com), has been retracted by agreement between the journal Editor in Chief and Wiley Periodicals, Ltd. The retraction has been agreed due to data duplication, both from previous papers from the same group (Shukla Y, Prasad S, Tripathi C, Singh M, George J, Kalra N. In vitro and in vivo modulation of testosterone mediated alterations in apoptosis related proteins by [6]‐gingerol. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2007;51(12):1492–1502. https://doi.org/10.1002/mnfr.200700197
as well as within the figures themselves, specifically figure 4 C, where the flow cytometry contains multiple intra‐figure duplications. The authors and the institution were both contacted by the publisher for explanations regarding the duplication and both were unresponsive.
LikeLike
2021 retraction of:
Pharm Res. 2009 Jan;26(1):211-7. doi: 10.1007/s11095-008-9723-z. Epub 2008 Sep 13.
Chemopreventive potential of resveratrol in mouse skin tumors through regulation of mitochondrial and PI3K/AKT signaling pathways
Preeti Roy 1, Neetu Kalra, Sahdeo Prasad, Jasmine George, Yogeshwer Shukla
Affiliations collapse
Affiliation
1Proteomics Laboratory, Indian Institute of Toxicology Research, (Council of Scientific & Industrial Research, India), P.O. Box 80, M.G. Marg, Lucknow, 226001, India.
PMID: 18791811 DOI: 10.1007/s11095-008-9723-z
2021 retraction note
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007%2Fs11095-020-02973-y
Retraction Note: Pharmaceutical Research volume 26, pages 211–217(2009)
https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-008-9723
The Editor-in-Chief has retracted this article [1] due to concerns about the reliability of the figures in this article. Specifically:
For Fig. 3A, the beta-actin band appears to be identical to figures from multiple other journals [2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
For Fig. 3C, an identical beta-actin band appears in Fig. 1B of [2] despite different conditions
For Fig. 3D, The first two and last two lanes of the beta-actin band appear to be identical
For Fig. 3D, the Cytochrome C blot appears to have be a duplication of the Apaf 1 band in Fig. 5B from [7]. Lanes III and IV seem to have been rotated and vertically stretched.
For Fig. 4C, the beta-actin band appears remarkably similar to Figs. 1 and 2 in [3]
For Fig. 5B, lanes I to V of the AKT blot appear to have been duplicated from lanes A to E in Fig. 2B of [3]. Lanes III and IV seem to have been rotated and vertically stretched.
Given these concerns, the Editor-in-Chief therefore no longer has confidence in the overall study presented in this article.
Authors Jasmine George and Yogeshwer Shukla do not agree with this retraction. Preeti Roy, Neetu Kalra, and Sahdeo Prasad have not responded to notices about this retraction.
1.
Roy, P., Kalra, N., Prasad, S. et al. Chemopreventive Potential of Resveratrol in Mouse Skin Tumors Through Regulation of Mitochondrial and PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathways. Pharm Res 26, 211–217 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-008-9723-z
2.
Arora, A., Siddiqui, I. A., & Shukla, Y. (2004). Modulation of p53 in 7, 12-dimethylbenz [a] anthracene–induced skin tumors by diallyl sulfide in Swiss albino mice. Molecular Cancer Therapeutics, 3(11), 1459–1466.
3.
Arora, A., Kalra, N., & Shukla, Y. (2006). Regulation of p21/ras protein expression by diallyl sulfide in DMBA induced neoplastic changes in mouse skin. Cancer letters, 242(1), 28–36.
4.
Shukla, Y., Prasad, S., Tripathi, C., Singh, M., George, J., & Kalra, N. (2007). In vitro and in vivo modulation of testosterone mediated alterations in apoptosis related proteins by [6]-gingerol. Molecular nutrition & food research,
51(12), 1492–1502.
5.
Kalra, N., Seth, K., Prasad, S., Singh, M., Pant, A. B., & Shukla, Y. (2007). Theaflavins induced apoptosis of LNCaP cells is mediated through induction of p53, down-regulation of NF-kappa B and mitogen-activated protein kinases pathways. Life sciences, 80(23), 2137–2146.
6.
Prasad, S., Kalra, N., & Shukla, Y. (2007). Induction of apoptosis by lupeol and mango extract in mouse prostate and LNCaP cells. Nutrition and cancer,
60(1), 120–130.
7.
Kalra, N., Roy, P., Prasad, S., & Shukla, Y. (2008). Resveratrol induces apoptosis involving mitochondrial pathways in mouse skin tumorigenesis. Life sciences, 82(7–8), 348–358.
LikeLike
05 April 2022 Expression of Concern for:
Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2010 Mar;65(4):687-96. doi: 10.1007/s00280-009-1074-x. Epub 2009 Jul 24.
Induction of apoptosis by [6]-gingerol associated with the modulation of p53 and involvement of mitochondrial signaling pathway in B[a]P-induced mouse skin tumorigenesis
Nidhi Nigam 1, Jasmine George, Smita Srivastava, Preeti Roy, Kulpreet Bhui, Madhulika Singh, Yogeshwer Shukla
Affiliation
1Proteomics Laboratory, Indian Institute of Toxicology Research (CSIR), M.G. Marg, P.O. Box 80, Lucknow 226001, India.
PMID: 19629484
DOI: 10.1007/s00280-009-1074-x
05 April Expression of Concern.
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00280-022-04426-2
Expression of Concern: Cancer Chemother Pharmacol (2010) 65:687–696 https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-009-1074-x
The Editors-in-Chief are issuing an Editorial Expression of Concern for this article [1]. Concerns were raised regarding similarities in figures in this article and previously published articles by Roy et al. [2] and Nigam et al. [3]. Specifically, it concerns:
The beta-actin band of Fig. 5 which appears to have similarities with the beta-actin band in Fig. 3 of Roy et al. (2009) [2].
The beta-actin band in Fig. 6 which has similarities with Fig. 3C (lanes b-h) of Roy et al. (2009) [2].
Lanes I, IVA and VA of the Bax band in Fig. 5 which are potentially identical to lanes II, III, and IV of the Apaf-1 band in Fig. 4B of Nigam et al. (2009) [3].
Lanes I, III, VA and VB of the Bcl2 band in Fig. 5 which have similarities with the entire Caspase-9 band in Fig. 4B of Nigam et al. (2009) [3].
Lanes II, IVA, IVB and VA of the Cytochrome-c band in Fig. 5 which are possibly identical to lanes I-IV of the Bax band in Fig. 4B of Nigam et al. (2009) [3].
Following an investigation, it was concluded that the conclusions of this article are still valid despite the potential replication, but the Editors-in-Chief would like to urge the readers to use caution when interpreting the results of the article.
Authors Jasmine George, Smita Srivastava, Kulpreet Bhui, Madhulika Singh & Yogeshwer Shukla have agreed to this Editorial Expression of Concern. The editor was not able to obtain current email addresses for Authors Preeti Roy and Nidhi Nigam.
References
Nigam N, George J, Srivastava S et al (2010) Induction of apoptosis by [6]-gingerol associated with the modulation of p53 and involvement of mitochondrial signaling pathway in B[a]P-induced mouse skin tumorigenesis. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 65:687–696. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-009-1074-x
Roy P, Nigam N, George J et al (2009) Induction of apoptosis by tea polyphenols mediated through mitochondrial cell death pathway in mouse skin tumors. Cancer Biol Ther 8(13):1281–1287. https://doi.org/10.4161/cbt.8.13.8728
Nigam N, Bhui K, Prasad S et al (2009) [6]-Gingerol induces reactive oxygen species regulated mitochondrial cell death pathway in human epidermoid carcinoma A431 cells. Chem Biol Interact 181(1):77–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2009.05.012
Author information
Affiliations
Proteomics Laboratory, Indian Institute of Toxicology Research (CSIR), M.G. Marg, P.O. Box 80, Lucknow, 226001, India
Nidhi Nigam, Jasmine George, Smita Srivastava, Preeti Roy, Kulpreet Bhui, Madhulika Singh & Yogeshwer Shukla
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Yogeshwer Shukla.
LikeLike
“The data were fake but the conclusion remains valid.”
LikeLike