This is a story of western blot, which might be holding the current record of re-use. While other papers are plagued by image duplications, this little western blot seems to have been used in a different context 12 times, in 10 papers, in 9 different journals. At least this is the current count. As the evidence suggests, the blot began its wandering adventures in 2006 and stood in for a different protein each time. It may have started as a western blot probed for glucose transporter GLUT4 or phosphotyrosine, but actually, it is now really hard to say what it may originally have been.
The wandering western blot’s owners are the Brazilian physiologists Mario José Abdalla Saad and his colleagues José Barreto Campello Carvalheira, Cláudio T. De Souza and Lício Augusto Velloso. I received the information from this, well, duodecuplication, from a concerned source whose identity I was asked to keep confidential. Therefore, I have assembled a PowerPoint file on this wandering western blot, with the corresponding editorial replies (or the lack of them) attached as presentation notes. The file is publicly accessible here.
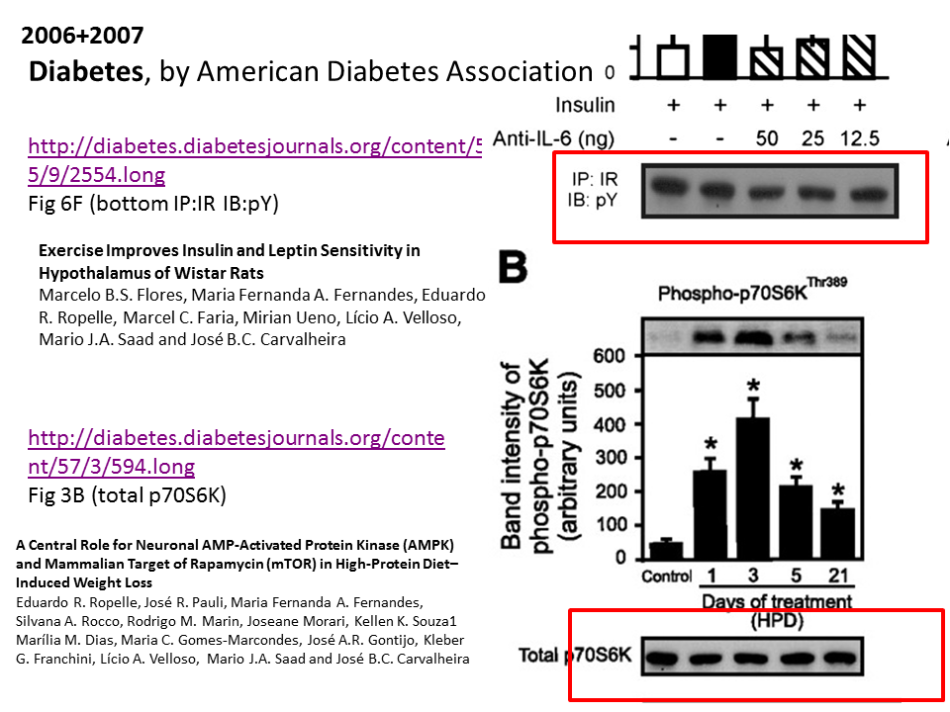
Mario Saad is medicine professor at the Brazilian State University of Campinas in São Paolo (Universidade Estadual de Campinas, UNICAMP) and member of the Brazilian Academy of Sciences. He is also somewhat of a celebrity on RetractionWatch. So far Saad had to retract one paper for plagiarism, issued a 12-figure correction in PLOS One and unsuccessfully sued the American Diabetes Association (ADA), publisher of the journal Diabetes, protesting against their Expression of Concern on four of his papers there. None of these papers has been retracted yet, while the Expression of Concern is already one year old. The wandering western blot also made into one of these Diabetes papers.
Saad himself, asked to address the wandering western blot issue, immediately replied to my email:
“I only can comment the manuscripts that I am the PI or the correspondent author.
These manuscripts were investigated by an independent commission, with scientists outside our University, and we showed that most of these allegations were false. We showed all the original gels and proved that what they accuse of duplicated images are, in most of the cases similar images coming from different gels. In a previous manuscript that we identified the same image, an unintentional mistake, we wrote to the journal and asked for correction. We invite people to come to our lab to check the original images”.
This is an example of the wandering western blot in a paper where Saad is corresponding author:
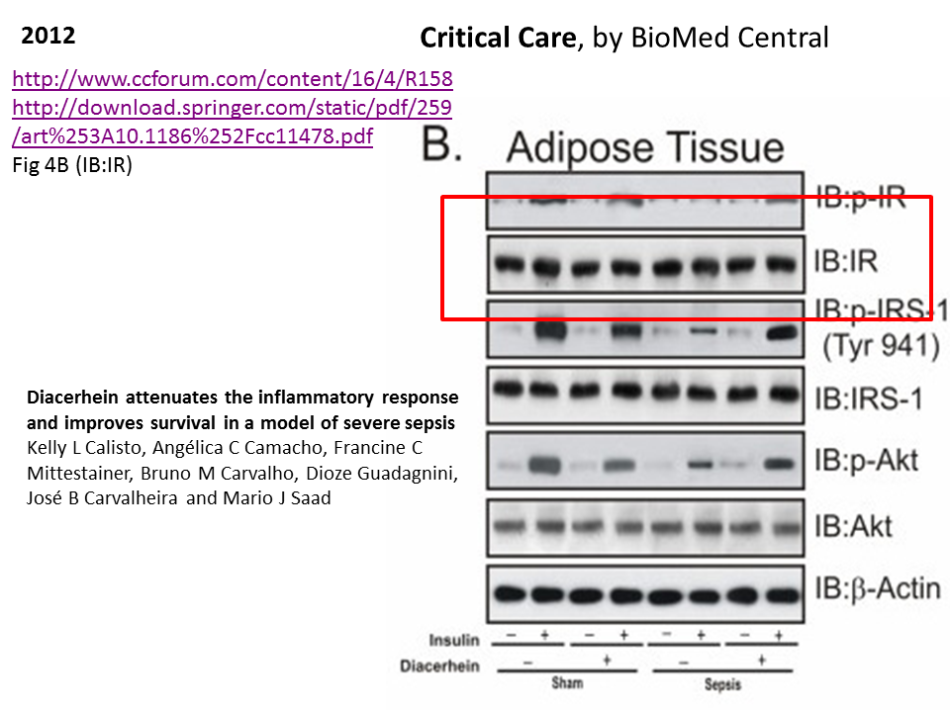
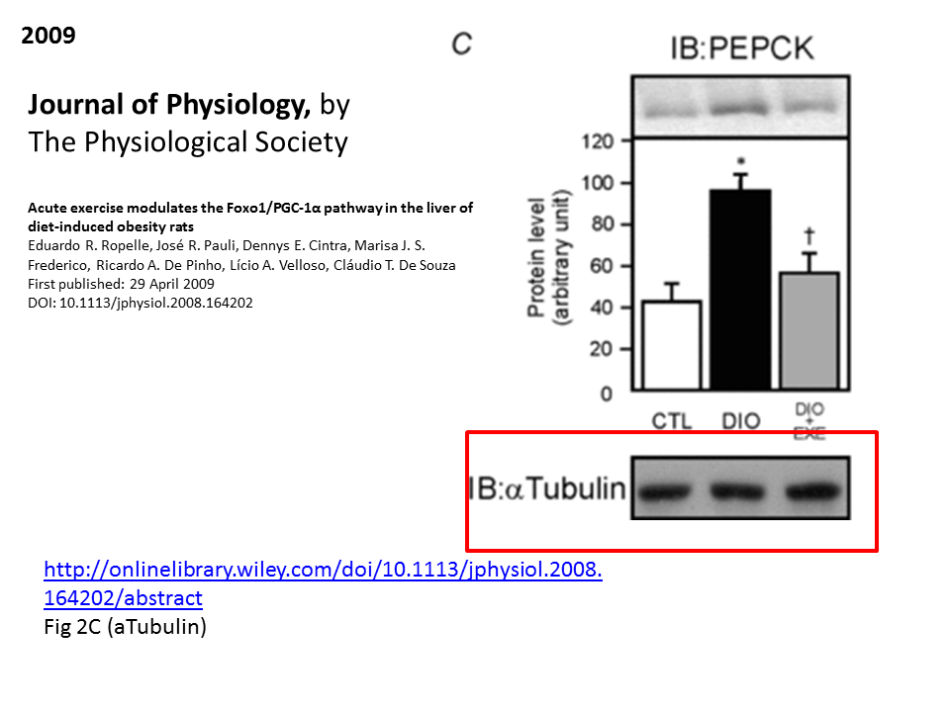
Remarkably, Saad is often not even a co-author on some of the papers featuring the wandering western blot. However, none of the other corresponding authors and Saad’s colleagues, namely Carvalheira, oncology professor at UNICAMP clinic, De Souza, physiology professor at Universidade do Extremo Sul Catarinense and Lício Velloso, Saad’s former postdoc, and now group leader at at UNICAMP, chose to reply my emails, despite a reminder. Therefore, it is unclear how the western blot made it into Saad-free papers like this one:
Saad and his UNICAMP colleagues were banned in 2014 by ADA from submitting papers to their journals. RetractionWatch indirectly quotes Christian Kohler, managing director and member of ADA’s Panel on Ethical Scientific Programs, as having informed in December 2014:
“Most detrimental, the ADA stated that it will not consider, for publication in any ADA journal any submissions authored by any of the faculty of the University until the issues described in the expression of concern have been appropriately reviewed and addressed by the University [UNICAMP,- LS]”.
To me, Kohler now wrote:
“The American Diabetes Association, the publisher of Diabetes, is aware of this issue, which is currently under review by the Association’s Panel of Ethical Scientific Programs (ESP). The ESP works on behalf of ADA journal editors to review potential instances of scientific or academic misconduct in manuscripts submitted to or published in ADA journals”.
Saad was exonerated by the first UNICAMP investigation, which results ADA did not recognize and insisted on a second one. Its outcome or even existence is unsure. Nevertheless, it seems that the ban is now history. Good evidence for it is that Velloso was welcome to publish a paper in Diabetes in October 2015.
There is indeed not enough evidence that the all editorial offices are taking the issue of data integrity in their Saad & Co papers seriously. Though I received a reply from 7 publishers, FEBS Letters and Life Sciences did not respond to my email at all. Here is what the University of Heidelberg-based FEBS Letters may or may not be investigating:

Also, while I was informed by the Deputy Director of Publications at Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology (FASEB), Cody Mooneyhan, that they “are moving this forward according to our editorial policies on misconduct”, my source completely failed to get through. To this anonymous informant, Mooneyhan wrote:
“It appears that you are accusing the authors of this paper of academic misconduct. We take these accusations very seriously, but we cannot accept them anonymously. (Please see the journal’s policies on misconduct.) If you wish to remain anonymous, we encourage you to contact the authors’ institution(s) directly with your concerns.
Otherwise, please submit a formal letter with the name and address of your institution (most letterheads will suffice), as well as a telephone number and an e-mail address from your institution where you may be reached. If you are not a researcher, professor, etc. affiliated with an institution, please submit a formal letter that includes your home address and telephone number”.
That is indeed an interesting attitude to processing evidence of potential misconduct, especially from the respectable FASEB. As I have not submitted any such formal letter either, I now wonder if my inquiry was accepted at all, and whether FASEB Journal will really follow this up:
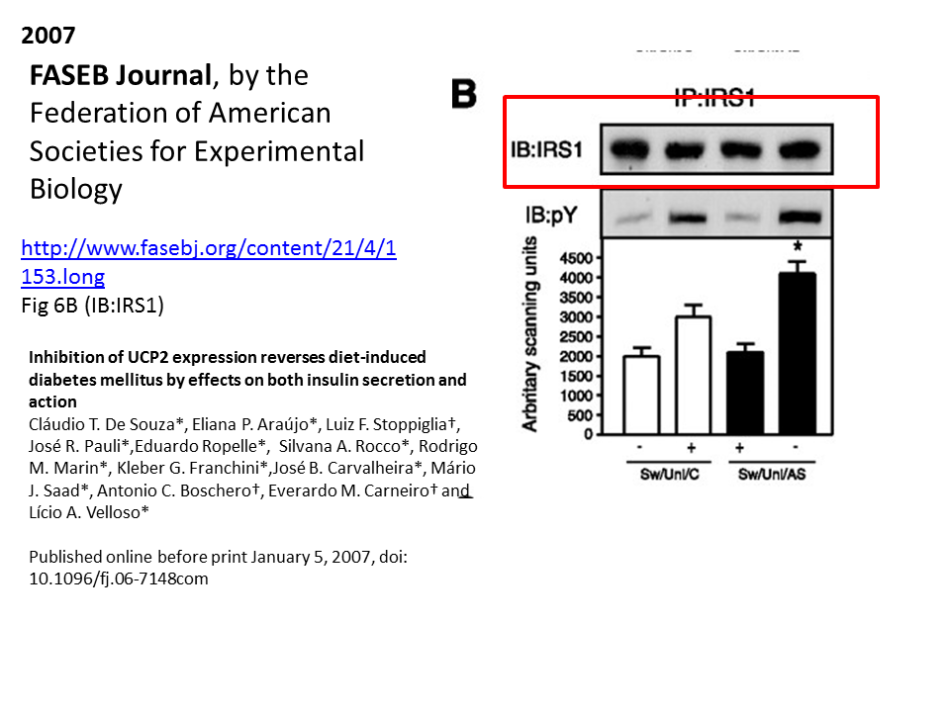
Some publishers however, like PLOS One, Gastroenterology, The Physiological Society and Endocrine Society, were somewhat more convincing, by claiming that investigations are already initiated (or about to). With PLOS One and Gastroenterology, the wandering western blot seems to feature even twice inside the same paper, standing in for JAK2 and STAT3 as well as IKKβ and IRβ, respectively.

I’m a bit confused. Though a couple of these look pretty identical the others really don’t look that similar (other than “there are bands there” kind of similarity). The first two examples (both from the journal Diabetes) are pretty clearly different blots- looking at the angles of the bands relative to each other makes that clear. It’s certainly possible that there might have been some image manipulation, but I don’t see a direct copying of a Western here. What’s the evidence that these are the same Western?
LikeLike
Hi Jason, with the Diabetes example you mention: the blot is shifted by one band. Also other examples are shifted. Use the band with the tiny dot under it as alignment orientation and note that the bands match in their shapes then (I assume my original source who flagged this did the same).
LikeLike
I also found that many of the comparisons made were inaccurate, or possibly even incorrect. Moreover, the red boxed bands, which are claimed to be identical, are not, something that Jason McDermott points out above. I think it is very important to have clearer evidence, including the tools that were used to derive this incredible conclusion (which, if false, could be a serious case of libel). How accurate and reliable is this “source”? I have downloaded the Power Point file. Please note, Dr. Schneider, if you decide to change any figures, then these must be newly represented. You cannot simply erase the above evidence and substitute files or images, because this is now a firm public accusation against Saad et al. As I say, in less than half of the cases, they could be similar bands, but even so, some are so blurred that I hesitate to use the terms “the same” or “identical”.
LikeLiked by 1 person
Someone on PubPeer did a much better job than myself in visualising this wandering western blot across 12 papers. I admit, my version was less obvious, and as such deserved criticism. But please see here:

https://pubpeer.com/publications/A8F83A3982B9C83C02D13B39AA0CAE#fb46905
LikeLike
Have bands, fly with me!
LikeLike
You are doing a great job!
LikeLike
I received this update from Lindsey M. Brounstein, Managing Editor at American Gastroenterological Association, which publishes the journal Gastroenterology. The reply suggest that the journal recognises the problem of image duplication and will act on it very soon. The wandering western blot appeared in this case in Flores et al, 2012:
LikeLike
One was retracted and another one subjected to an expression of concern at the current issue of Diabetes
LikeLike
Reuse of mice blots in this human study by Saad:
https://pubpeer.com/publications/52629108BC6FB0F463158204D10123
LikeLike
Likely they have a mouse infestation in the building and the pest controller has not been effective. In these most difficult circumstances, a cat can work well.
LikeLike
Another one was corrected
http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0024320516302004
LikeLike
Pingback: Image integrity concerns in papers from a Pfizer lab – For Better Science
Another earned an expression of concern (along to three unrelated articles):
http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1113/JP272727/pdf
LikeLike
Pingback: Researcher who unsuccessfully sued journal to stop retractions earns another expression of concern - Retraction Watch at Retraction Watch
Sally Howells, managing editor at Journal of Physiology informed me now that “four Expressions of Concern have been issued.
http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1113/JP272726/full
http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1113/JP272728/full
http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1113/JP272727/full
http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1113/JP272710/full
The University is investigating the case further”.
LikeLike
PLOS Biology retracts on 23 May 2016 the paper
Caricilli AM, Picardi PK, de Abreu LL, Ueno M, Prada PO, et al. (2011) Gut Microbiota Is a Key Modulator of Insulin Resistance in TLR 2 Knockout Mice. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1001212
http://journals.plos.org/plosbiology/article?id=info:doi/10.1371/journal.pbio.1001212
LikeLike
These type of flaws are really very common. As an example:
https://pubpeer.com/publications/22635005
LikeLike
Pingback: União Europeia quer todos os seus artigos científicos em acesso aberto até 2020 | Direto da Ciência
Here another reason for anonymous PPPR: editors are far from being objective many times….
LikeLike
Something that I find annoying is that the journals allow the authors, during corrections/retractions, to state that the image manipulations/duplications were made, several/many times, “inadvertently”… lack of honesty over lack of honesty…
LikeLike
Yes….actually editors get to the point of “designing” the manuscripts together with the authors much time before the publication….
We recently sent an anonymously complaint to the respective editors regarding the manuscripts mentioned bellow:
https://pubpeer.com/publications/8F2A681C84FB1D9FC6A9D0B46F5E0A
https://pubpeer.com/publications/25985394
https://pubpeer.com/publications/22635005
Lets wait and see what response we get from them
LikeLike
It is not good that Hector Peinado did not reply to the accusations on blot duplications (rotations)… The names of David Lynden and Jacqueline Broomberg are starting to sound familiar to me, not for good reasons, obviously, since my memory seems to associate them with Pubpeer…
LikeLike
Neither they respond to the IF problems in Costa-Silva et al, 2015 unfortunately…big disillusion….
LikeLike
After the Voinnet gel/band scandal, it seems that we also have a “wondering band/gel” problem in plant science.
Here is the latest case (not as bad as Saad, but worrisome nonetheless).
ISRN Agronomy, vol. 2013, Article ID 284830, 15 pages, 2013.
Dibyendu Talukdar
Growth Responses and Leaf Antioxidant Metabolism of Grass Pea (Lathyrus sativus L.) Genotypes under Salinity Stress
doi: 10.1155/2013/284830
http://www.hindawi.com/journals/isrn/2013/284830/
https://www.pubpeer.com/publications/F4C1CEC4F85DA6A889636EFDB66B33
Agricultural Research December 2013, Volume 2, Issue 4, pp 330-339
Plant Growth and Leaf Antioxidant Metabolism of Four Elite Grass Pea (Lathyrus sativus) Genotypes, Differing in Arsenic Tolerance
Dibyendu Talukdar
DOI: 10.1007/s40003-013-0085-3
http://link.springer.com/article/10.1007%2Fs40003-013-0085-3
https://www.pubpeer.com/publications/2301D6B639356515DE3681DC9F6559
LikeLike
Retraction
ISRN Agronomy, vol. 2013, Article ID 284830, 15 pages, 2013.
Growth Responses and Leaf Antioxidant Metabolism of Grass Pea (Lathyrus sativus L.) Genotypes under Salinity Stress
Dibyendu Talukdar
doi: 10.1155/2013/284830
http://www.hindawi.com/journals/isrn/2013/284830/
“International Scholarly Research Notices has retracted this article. The article was found to contain images with signs of duplication and manipulation in Figures 5(a), 5(b), 6(a), and 6(b), and duplication from Talukdar D. Plant Growth and Leaf Antioxidant Metabolism of Four Elite Grass Pea (Lathyrus sativus) Genotypes, Differing in Arsenic Tolerance. Agric Res (2013) 2: 330. doi:10.1007/s40003-013-0085-3 in Figure 6.”
LikeLike